Biochemical characterization of the Yersinia YopT protease: cleavage site and recognition elements in Rho GTPases
- PMID: 12538863
- PMCID: PMC298699
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252770599
Biochemical characterization of the Yersinia YopT protease: cleavage site and recognition elements in Rho GTPases
Abstract
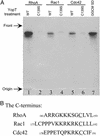
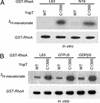
The Gram-negative bacterial pathogen Yersinia delivers six effector proteins into the host cells to thwart the host innate immune response. One of the effectors, YopT, causes the disruption of the actin cytoskeleton and contributes to the inhibition of phagocytosis of the pathogen. YopT functions as a cysteine protease to cleave Rho family GTPases. We have analyzed the YopT cleavage products of Rho GTPases by TLC and determined their chemical structure by MS. Amino acid labeling experiments were performed to locate the exact site in RhoA where the YopT cleavage occurs. Our data unambiguously demonstrate that YopT cleaves N-terminal to the prenylated cysteine in RhoA, Rac, and Cdc42 and that the cleavage product of the GTPases is geranylgeranyl cysteine methyl ester. YopT cleaves GTP- and GDP-bound forms of RhoA equally, suggesting that the cleavage does not depend upon the conformation status of the GTPases. YopT also cleaves both farnesylated and geranylgeranylated forms of RhoA. The polybasic sequence in the C terminus of RhoA is essential for YopT substrate recognition and cleavage.
Figures
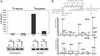


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

