Computational design of a water-soluble analog of phospholamban
- PMID: 12538897
- PMCID: PMC2312418
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0226603
Computational design of a water-soluble analog of phospholamban
Abstract
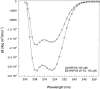
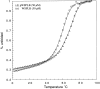
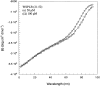
Membrane proteins and water-soluble proteins share a similar core. This similarity suggests that it should be possible to water-solubilize membrane proteins by mutating only their lipid-exposed residues. We have developed computational tools to design water-soluble variants of helical membrane proteins, using the pentameric phospholamban (PLB) as our test case. To water-solublize PLB, the membrane-exposed positions were changed to polar or charged amino acids, while the putative core was left unaltered. We generated water-soluble phospholamban (WSPLB), and compared its properties to its predecessor PLB. In aqueous solution, WSPLB mimics all of the reported properties of PLB including oligomerization state, helical structure, and stabilization upon phosphorylation. We also characterized the truncated mutant WSPLB (21-52) comprising only the former transmembrane segment of PLB. This peptide shows a decreased specificity for forming a pentameric oligomerization state.
Figures






Similar articles
-
De novo design of a pentameric coiled-coil: decoding the motif for tetramer versus pentamer formation in water-soluble phospholamban.J Pept Res. 2005 Mar;65(3):312-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.2005.00244.x. J Pept Res. 2005. PMID: 15787961
-
X-ray structure of a water-soluble analog of the membrane protein phospholamban: sequence determinants defining the topology of tetrameric and pentameric coiled coils.J Mol Biol. 2005 May 6;348(3):777-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.040. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15826670
-
Toward a high-resolution structure of phospholamban: design of soluble transmembrane domain mutants.Biochemistry. 2000 Jun 13;39(23):6825-31. doi: 10.1021/bi0000972. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10841762
-
Structural perspectives of phospholamban, a helical transmembrane pentamer.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1997;26:157-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.26.1.157. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1997. PMID: 9241417 Review.
-
Modeling transmembrane helical oligomers.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997 Aug;7(4):486-94. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80111-x. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997. PMID: 9266169 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of a water-soluble transmembrane receptor kinase with intact molecular function by QTY code.Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 10;15(1):4293. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48513-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38858360 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Simulation of WSK-3, a Computationally Designed, Water-Soluble Variant of the Integral Membrane Protein KcsA.Biophys J. 2006 Feb 15;90(4):1156-63. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.068965. Epub 2005 Nov 18. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16299086 Free PMC article.
-
QTY code enables design of detergent-free chemokine receptors that retain ligand-binding activities.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 11;115(37):E8652-E8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811031115. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30154163 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Design: From the Aspect of Water Solubility and Stability.Chem Rev. 2022 Sep 28;122(18):14085-14179. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00757. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35921495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solubilization and humanization of paraoxonase-1.J Lipids. 2012;2012:610937. doi: 10.1155/2012/610937. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Lipids. 2012. PMID: 22720164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arkin, I.T., Rothman, M., Ludlam, C.F., Aimoto, S., Engelman, D.M., Rothschild, K.J., and Smith, S.O. 1995. Structural model of the phospholamban ion channel complex in phospholipid membranes. J. Mol. Biol. 248 824–834. - PubMed
-
- Boice, J.A., Dieckmann, G.R., DeGrado, W.F., and Fairman, R. 1996. Thermodynamic analysis of a designed three-stranded coiled coil. Biochemistry 35 14480–14485. - PubMed
-
- Bowie, J.U. 1997. Helix packing in membrane proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 272 780–789. - PubMed
-
- Brittsan, A.G., Carr, A.N., Schmidt, A.G., and Kranias, E.G. 2000. Maximal inhibition of SERCA2 Ca2+ affinity by phospholamban in transgenic hearts overexpressing a non-phosphorylatable form of phospholamban. J. Biol. Chem. 275 12129–12135. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

