A reinterpretation of the dimerization interface of the N-terminal domains of STATs
- PMID: 12538899
- PMCID: PMC2312425
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.0218903
A reinterpretation of the dimerization interface of the N-terminal domains of STATs
Abstract
The crystal structures of the N-terminal domain (N-domain) and the core region of the STAT family of transcription factors have been determined previously. STATs can form cooperative higher order structures (tetramers or higher oligomers) while bound to DNA. The crystal packing in the STAT4 N-domain crystal structure, determined at 1.5 A resolution, suggests two alternate organizations of the N-domain dimer. We now present the results of site directed mutagenesis of residues predicted to be involved at each dimer interface. Our results indicate that the dimer interface suggested earlier as being physiologically relevant is, in fact, unlikely to be so. Given the alternative model for the N-domain dimer, the ability of the N-domain to mediate interactions of two STAT dimers on DNA remains unchanged.
Figures
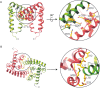

References
-
- Becker, S., Groner, B., and Muller, C.W. 1998. Three-dimensional structure of the Stat3β homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 394145–151. - PubMed
-
- Carson, M. 1991. RIBBONS 2.0. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24 958–961.
-
- Chen, X., Vinkemeier, U., Zhao, Y., Jeruzalmi, D., Darnell, Jr., J.E., and Kuriyan, J. 1998. Crystal structure of a tyrosine phosphorylated STAT-1 dimer bound to DNA. Cell 93 827–839. - PubMed
-
- Darnell, Jr., J.E. 1997. STATs and gene regulation. Science 277 1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Darnell, Jr., J.E., Kerr, I.M., and Stark, G.R. 1994. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264 1415–1421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

