Effect of inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 pathway on apoptosis and bcl-2 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected AGS cells
- PMID: 12540563
- PMCID: PMC145367
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.830-837.2003
Effect of inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 pathway on apoptosis and bcl-2 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected AGS cells
Abstract
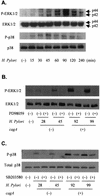
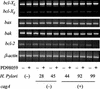
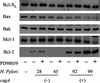
Helicobacter pylori induces activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). However, its effect on H. pylori-induced apoptosis has not been evaluated. Thus, we examined whether H. pylori-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) and p38 MAPK activation affects gastric epithelial cell apoptosis and bcl-2 family gene expression, especially in relation to the cagA status of an H. pylori strain. In flow cytometric and oligonucleosome-bound DNA enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analyses, infection with cagA(+) H. pylori strains induced gastric cancer cell apoptosis in AGS cells more prominently than infection with cagA mutants. Activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPKs was also more prominent in cagA(+) strains. Pretreatment with a MEK inhibitor (PD98059) inhibited ERK1/2 activation and increased H. pylori-induced apoptosis significantly. This increased apoptosis was accompanied by decreased antiapoptotic bcl-2 mRNA expression among bcl-2-related genes (bcl-2, bax, bak, mcl-1, and bcl-X(L/S)), and the effect was also more prominent in the cagA(+) strains. However, the alteration of bcl-2 gene expression was not accompanied by protein level changes. Inhibition of p38 using specific inhibitor SB203580 decreased H. pylori-induced apoptosis but resulted in little alteration of bcl-2-related gene expression. In conclusion, H. pylori-induced ERK1/2 activation, especially by the cagA(+) H. pylori strain, may play a protective role against gastric epithelial cell apoptosis partially through maintenance of bcl-2 gene expression.
Figures

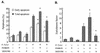


References
-
- Adams, J. M., and S. Cory. 1998. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322-1326. - PubMed
-
- Boucher, M. J., J. Morisset, P. H. Vachon, J. C. Reed, J. Laine, and N. Rivard. 2000. MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of human pancreatic cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 79:355-369. - PubMed
-
- Buckley, S., B. Driscoll, L. Barsky, K. Weinberg, K. Anderson, and D. Warburton. 1999. ERK activation protects against DNA damage and apoptosis in hyperoxic rat AEC2. Am. J. Physiol. 277:L159-L166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

