Patient specific quality assurance for the delivery of intensity modulated radiotherapy
- PMID: 12540817
- PMCID: PMC5724432
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v4i1.2540
Patient specific quality assurance for the delivery of intensity modulated radiotherapy
Abstract
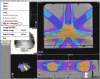
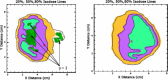
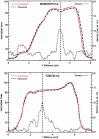
A patient specific quality assurance program has been developed to facilitate the clinical implementation of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) delivered using a micro-multileaf collimator. The methodology includes several dosimetric tasks that are performed prior to the treatment of each patient. Film dosimetry is performed for each individual field and for the multifield composite plan. Individual field measurements are performed at a depth of 5 cm in a water equivalent slab phantom; export of dose calculations from the treatment planning system is similarly specified. For the composite distribution, parameters from the patient plan are applied to an IMRT phantom, and film is exposed in an axial orientation. Distributions are compared with the aid of software developed for the specific tasks. The measured and calculated dose distributions can be superimposed and positioned graphically using move, rotate, and mirror tools, as well as by specifying isocenter coordinates and using fiducial marks. Horizontal and vertical profiles are available for analysis. Dose difference, distance-to-agreement, and gamma index, the minimum scaled multidimensional distance between a measurement and a calculation point determined in combined dose and physical distance space, are calculated along a specified isodose line and displayed. gamma provides an excellent measure of disagreement between measurement and calculation for complex intensity distributions. We specify 3% dose difference and 3 mm distance as our scaling acceptability criteria. Absolute dosimetry for each composite plan is performed using an ionization chamber. To date, excellent agreement between measurements and calculations has been observed.
Figures







References
-
- Burman C., Chui C. S., Kutcher G., Leibel S., Zelefsky M., LoSasso T., Spirou S., Wu Q., Yang J., Stein J., Mohan R., Fuks Z., and Ling C. C., “Planning, delivery, and quality assurance of intensity‐modulated radiotherapy using dynamic multileaf collimator: a strategy for large‐scale implementation for the treatment of carcinoma of the prostate,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. 39, 863–873 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Cardinale R. M., Benedict S. H., Wu Q., Zwicker R. D., Gaballa H. E., and Mohan R., “A comparison of three stereotactic radiotherapy techniques; ARCS vs. noncoplanar fixed field vs. intensity modulation,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. 42, 431–436 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Pickett B., Vigneault E., Kurhanewicz J., Verhey L., and Roach M., “Static field intensity modulation to treat a dominant intra‐prostatic lesion to 90 Gy compared to seven field 3‐dimensional radiotherapy,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. 44, 921–929 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Reinstein L. E., Wang X. H., Burman C. M., Chen Z., Mohan R., Kutcher G., Leibel S. A., and Fuks Z., “A feasibility study of automated inverse treatment planning for cancer of the prostate,” Int. J. Radiat. Oncol., Biol., Phys. 40, 207–214 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Verhey L. J., “Comparison of three‐dimensional conformal radiation therapy and intensity‐modulated radiation therapy systems,” Semin. Oncol. 9, 78–98 (1999). - PubMed

