In silico characterisation and chromosomal localisation of human RRH (peropsin)--implications for opsin evolution
- PMID: 12542842
- PMCID: PMC149353
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-4-3
In silico characterisation and chromosomal localisation of human RRH (peropsin)--implications for opsin evolution
Abstract
Background: The vertebrate opsins are proteins which utilise a retinaldehyde chromophore in their photosensory or photoisomerase roles in the visual/irradiance detection cycle. The majority of the opsins, such as rod and cone opsins, have a very highly conserved gene structure suggesting a common lineage. Exceptions to this are RGR-opsin and melanopsin, whose genes have very different intron insertion positions. The gene structure of another opsin, peropsin (retinal pigment epithelium-derived rhodopsin homologue, RRH) is unknown.
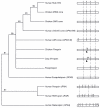
Results: By in silico analysis of the GenBank database we have determined that the human RRH comprises 7 exons spanning approximately 16.5 kb and is localised to chromosome 4q25 in the following gene sequence: cen-EGF-RRH-IF-qter - a position that excludes this gene as a candidate for the RP29 autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa locus. A comparison of opsin gene structures reveals that RRH and RGR share two common intron (introns 1 and 4) insertion positions which may reflect a shared ancestral gene.
Conclusion: The opsins comprise a diverse group of genes which appear to have arisen from three different lineages. These lineages comprise the "classical opsin superfamily" which includes the rod and cone opsins, pinopsin, VA-opsin, parapinopsin and encephalopsin; the RRH and RGR group; and the melanopsin line. A common lineage for RRH and RGR, together with their sites of expression in the RPE, indicates that peropsin may act as a retinal isomerase.
Figures

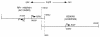

Similar articles
-
A human opsin-related gene that encodes a retinaldehyde-binding protein.Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 8;33(44):13117-25. doi: 10.1021/bi00248a022. Biochemistry. 1994. PMID: 7947717
-
Evolutionary Constraint on Visual and Nonvisual Mammalian Opsins.J Biol Rhythms. 2021 Apr;36(2):109-126. doi: 10.1177/0748730421999870. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Biol Rhythms. 2021. PMID: 33765865 Free PMC article.
-
Peropsin modulates transit of vitamin A from retina to retinal pigment epithelium.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21407-21416. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.812701. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29109151 Free PMC article.
-
The opsins.Genome Biol. 2005;6(3):213. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-3-213. Epub 2005 Mar 1. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 15774036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cone visual pigments.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 May;1837(5):664-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Sep 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24021171 Review.
Cited by
-
An extended family of novel vertebrate photopigments is widely expressed and displays a diversity of function.Genome Res. 2015 Nov;25(11):1666-79. doi: 10.1101/gr.189886.115. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26450929 Free PMC article.
-
Type II Opsins in the Eye, the Pineal Complex and the Skin of Xenopus laevis: Using Changes in Skin Pigmentation as a Readout of Visual and Circadian Activity.Front Neuroanat. 2022 Jan 21;15:784478. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2021.784478. eCollection 2021. Front Neuroanat. 2022. PMID: 35126061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human Müller cell line MIO-M1 expresses opsins.Mol Vis. 2011;17:2738-50. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22065927 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular and cellular basis of rhodopsin retinitis pigmentosa reveals potential strategies for therapy.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 Jan;62:1-23. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29042326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of irradiance detection: melanopsin and the non-visual opsins.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Oct 12;364(1531):2849-65. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0050. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19720649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lythgoe JN. The Ecology of Vision Oxford: Clarendon Press. 1979.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

