MC21-A, a bactericidal antibiotic produced by a new marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica sp. nov. O-BC30(T), against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 12543647
- PMCID: PMC151744
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.2.480-488.2003
MC21-A, a bactericidal antibiotic produced by a new marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica sp. nov. O-BC30(T), against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
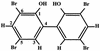
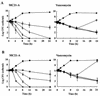
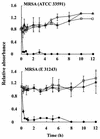
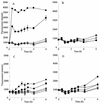
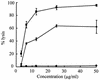
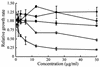
We previously reported a new marine bacterium, Pseudoalteromonas phenolica sp. nov. O-BC30(T), which produced a bactericidal antibiotic against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In the present study, we purified an anti-MRSA substance (MC21-A) from the methanol extract of the cells of P. phenolica O-BC30(T) and analyzed its chemical structure. MC21-A was determined to be 3,3',5,5'-tetrabromo-2,2'-biphenyldiol by spectrometric analyses. Its anti-MRSA activity against 10 clinical isolates of MRSA was comparable to that of vancomycin (MC21-A MICs, 1 to 2 micro g/ml; vancomycin MICs, <0.25 to 2 micro g/ml). This substance was also high active against Enterococcus serolicida, Enterococcus faecium, and Enterococcus faecalis but was less active against Streptococcus spp. A time-kill study also demonstrated that MC21-A was bactericidal and that its killing rate was much higher than that of vancomycin. The postantibiotic effect (PAE) of MC21-A against a clinical MRSA isolate, strain E 31243, was also comparable to that of vancomycin (MC21-A PAEs, 1.46 to 1.65 h; vancomycin PAEs, 0.84 to 1.43 h). However, a lysis experiment demonstrated that this substance failed to lyse MRSA cells. This substance also did not lyse human erythrocytes. A SYTOX Green staining experiment implied that this substance permeabilized the cell membrane of MRSA as its mode of action. When its activities against a hypersensitive Escherichia coli mutant (KO 1489) and wild-type strains were tested, MC21-A exhibited higher levels of activity against the former. Furthermore, MC21-A was not cytotoxic to human normal fibroblast, rat pheochromocytoma, and Vero cells at concentrations up to 50 micro g/ml. These results suggest that MC21-A might be useful as a lead compound in the development of new types of anti-MRSA substances with modes of action different from those of vancomycin and teicoplanin.
Figures
References
-
- Acebal, C., L. M. Cañedo, J. L. F. Puentes, J. P. Baz, F. Romero, F. De La Calle, M. D. G. Grávalos, and P. Rodrigues. 1999. Agrochelin, a new cytotoxic antibiotic from a marine agrobacterium. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physicochemical properties and biological activity. J. Antibiot. 52:983-987. - PubMed
-
- Acebal, C., R. Alcazar, L. M. Cañedo, F. De La Calle, P. Rodriguez, F. Romero, and J. L. F Puentes. 1998. Two marine agrobacterium producers of sesbanimide antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 51:64-67. - PubMed
-
- Barrett, J. F., R. M. Goldschmidt, L. E. Lawrence, B. Foleno, R. Chen, J. P. Demers, S. Johnson, R. Konojia, J. Fernandez, J. Bernstein, L. Licata, A. Donetz, S. Huang, D. J. Hlasta, M. J. Macielag, K. Ohemeng, R. Frechette, M. B. Frosco, D. H. Klaubert, J. M. Whiteley, L. Wang, and J. A. Hoch. 1998. Antibacterial agents that inhibit two-component signal transduction systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:5317-5322. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

