Toward the development of a virus-cell-based assay for the discovery of novel compounds against human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 12543650
- PMCID: PMC151745
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.2.501-508.2003
Toward the development of a virus-cell-based assay for the discovery of novel compounds against human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
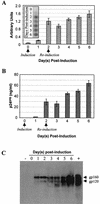
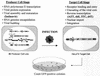
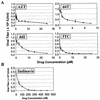
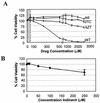
The emergence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains resistant to highly active antiretroviral therapy necessitates continued drug discovery for the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Most current drug discovery strategies focus upon a single aspect of HIV-1 replication. A virus-cell-based assay, which can be adapted to high-throughput screening, would allow the screening of multiple targets simultaneously. HIV-1-based vector systems mimic the HIV-1 life cycle without yielding replication-competent virus, making them potentially important tools for the development of safe, wide-ranging, rapid, and cost-effective assays amenable to high-throughput screening. Since replication of vector virus is typically restricted to a single cycle, a crucial question is whether such an assay provides the needed sensitivity to detect potential HIV-1 inhibitors. With a stable, inducible vector virus-producing cell line, the inhibitory effects of four reverse transcriptase inhibitors (zidovudine, stavudine, lamivudine, and didanosine) and one protease inhibitor (indinavir) were assessed. It was found that HIV-1 vector virus titer was inhibited in a single cycle of replication up to 300-fold without affecting cell viability, indicating that the assay provides the necessary sensitivity for identifying antiviral molecules. Thus, it seems likely that HIV-1-derived vector systems can be utilized in a novel fashion to facilitate the development of a safe, efficient method for screening compound libraries for anti-HIV-1 activity.
Figures


References
-
- Balzarini, J., A. van Aerschot, P. Herdewijn, and E. De Clercq. 1989. 5-Chloro-substituted derivatives of 2′,3′-didehydro-2′,3′-dideoxyuridine, 3′-fluoro-2′,3′-dideoxyuridine and 3′-azido-2′,3′-dideoxyuridine as anti-HIV agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 38:869-874. - PubMed
-
- Berger, J., J. Hauber, R. Hauber, R. Geiger, and B. R. Cullen. 1988. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene 66:1-10. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J. C., T. Friedmann, W. Driever, M. Burrascano, and J. K. Yee. 1993. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:8033-8037. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carr, A., J. Miller, M. Law, and D. A. Cooper. 2000. A syndrome of lipoatrophy, lactic acidaemia and liver dysfunction associated with HIV nucleoside analogue therapy: contribution to protease inhibitor-related lipodystrophy syndrome. AIDS 14:F25-F32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

