The antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus causes membrane permeabilization
- PMID: 12543664
- PMCID: PMC151754
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.2.588-593.2003
The antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus causes membrane permeabilization
Abstract
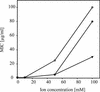
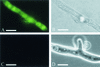
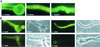
We investigated the inhibitory effects of the antifungal protein (AFP) from Aspergillus giganteus on the growth of several filamentous fungi. For this purpose, the MICs of AFP were determined and ranged from 0.1 micro g/ml for Fusarium oxysporum to 200 micro g/ml for Aspergillus nidulans. The antifungal activity of AFP was diminished in the presence of cations. We were able to show that incubation of AFP-sensitive fungi with the protein resulted in membrane permeabilization using an assay based on the uptake of the fluorescent dye SYTOX Green. No permeabilization by AFP could be detected at concentrations below the species-specific MIC. Furthermore, AFP-induced permeabilization could readily be detected after 5 min of incubation. Localization experiments with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled AFP and immunofluorescence staining with an AFP-specific antibody supported the observation that the protein interacts with membranes. After treatment of AFP-sensitive fungi with AFP, the protein was localized at the plasma membrane, whereas it was mainly detected inside the cells of AFP-resistant fungi. We conclude from these data that the growth-inhibitory effect of AFP is caused by permeabilization of the fungal membranes.
Figures
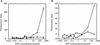
References
-
- Campos-Olivas, R., M. Bruix, J. Santoro, A. Martinez del Pozo, J. Lacadena, J. G. Gavilanes, and M. Rico. 1996. Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism and substrate specificity of the ribonuclease alpha-sarcin. FEBS Lett. 399:163-165. - PubMed
-
- Campos-Olivas, R., M. Bruix, J. Santoro, J. Lacadena, A. Martinez del Pozo, J. G. Gavilanes, and M. Rico. 1995. NMR solution structure of the antifungal protein from Aspergillus giganteus: evidence for cysteine pairing isomerism. Biochemistry 34:3009-3021. - PubMed
-
- Cociancich, S., A. Ghazi, C. Hetru, J. A. Hoffmann, and L. Letellier. 1993. Insect defensin, an inducible antibacterial peptide, forms voltage-dependent channels in Micrococcus luteus. J. Biol. Chem. 268:19239-19245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

