Sterilizing activities of fluoroquinolones against rifampin-tolerant populations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 12543673
- PMCID: PMC151758
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.2.653-657.2003
Sterilizing activities of fluoroquinolones against rifampin-tolerant populations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
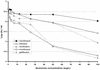
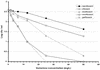
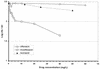
The bactericidal activities of ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and gatifloxacin were tested in three models of rifampin-tolerant Mycobacterium tuberculosis persisters. Model 1 was a 100-day-old, unshaken, anaerobically adapted culture in which serial dilutions of the quinolones were incubated for 5 days and CFU counts were then done In models 2 and 3, 100 mg of rifampin/liter was added to the 100-day culture for 5 or 7 days to produce tolerant organisms that did not grow on plates; the rifampin was then washed off, fresh medium was added to allow recovery of growth on plates, and the culture was incubated for 7 days before CFU counts. In model 2, the quinolones were added after rifampin had been washed off, whereas in model 3 the quinolones were added to the cultures containing rifampin. In models 1 and 2, ciprofloxacin had the least bactericidal activity, ofloxacin and levofloxacin had greater activities, and moxifloxacin and gatifloxacin had the greatest activities. In model 3, ofloxacin had no detectable activity whereas moxifloxacin killed about log(10) 0.279 CFU of the persisters per ml at concentrations attainable in lesions; isoniazid had virtually no activity. These findings predict that ofloxacin will not be found to have effective sterilizing activity in clinical studies now planned whereas moxifloxacin will be able to shorten treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bactericidal action of gatifloxacin, rifampin, and isoniazid on logarithmic- and stationary-phase cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Feb;49(2):627-31. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.627-631.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15673743 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal activity of moxifloxacin on exponential and stationary phase cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Chemother. 2009 Apr;21(2):127-34. doi: 10.1179/joc.2009.21.2.127. J Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19423464
-
Bactericidal action of ofloxacin, sulbactam-ampicillin, rifampin, and isoniazid on logarithmic- and stationary-phase cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Oct;40(10):2296-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.40.10.2296. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996. PMID: 8891133 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for development of new antimycobacterial drugs, with special reference to a new benzoxazinorifamycin, KRM-1648.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000;48(3):183-8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2000. PMID: 10912623 Review.
-
Prospects for development of new antimycobacterial drugs.J Infect Chemother. 2000 Mar;6(1):8-20. doi: 10.1007/s101560050043. J Infect Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11810525 Review.
Cited by
-
Moxifloxacin population pharmacokinetics in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and the effect of intermittent high-dose rifapentine.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Aug;56(8):4471-3. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00404-12. Epub 2012 May 14. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22585223 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fluoroquinolone susceptibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis after pre-diagnosis exposure to older- versus newer-generation fluoroquinolones.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Sep;42(3):232-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.04.027. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23806638 Free PMC article.
-
Early bactericidal activity of moxifloxacin in treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis: a prospective, randomized study.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Mar;48(3):780-2. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.3.780-782.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 14982764 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of the penetration of antituberculosis agents in rabbit pulmonary lesions.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jan;56(1):446-57. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05208-11. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 21986820 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective comparison of levofloxacin and moxifloxacin on multidrug-resistant tuberculosis treatment outcomes.Korean J Intern Med. 2011 Jun;26(2):153-9. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2011.26.2.153. Epub 2011 Jun 1. Korean J Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21716591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coates, A., Y. Hu, R. Bax, and C. Page. 2002. The future challenges facing the development of new antimicrobial drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 1:895-910. - PubMed
-
- Global Alliance for Tuberculosis Drug Development. 2001. Tuberculosis scientific blueprint for TB drug development. Tuberculosis 81(Suppl. 1):1-52. - PubMed
-
- Hu, Y., and A. R. M. Coates. 2001. Increased levels of sigJ mRNA in late stationary phase cultures of Mycobacterium tuberculosis detected by DNA array hybridisation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 202:59-65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

