AcrAB multidrug efflux pump is associated with reduced levels of susceptibility to tigecycline (GAR-936) in Proteus mirabilis
- PMID: 12543675
- PMCID: PMC151746
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.2.665-669.2003
AcrAB multidrug efflux pump is associated with reduced levels of susceptibility to tigecycline (GAR-936) in Proteus mirabilis
Abstract
Tigecycline has good broad-spectrum activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens with the notable exception of the PROTEEAE: A study was performed to identify the mechanism responsible for the reduced susceptibility to tigecycline in Proteus mirabilis. Two independent transposon insertion mutants of P. mirabilis that had 16-fold-increased susceptibility to tigecycline were mapped to the acrB gene homolog of the Escherichia coli AcrRAB efflux system. Wild-type levels of decreased susceptibility to tigecycline were restored to the insertion mutants by complementation with a clone containing a PCR-derived fragment from the parental wild-type acrRAB efflux gene cluster. The AcrAB transport system appears to be associated with the intrinsic reduced susceptibility to tigecycline in P. mirabilis.
Figures
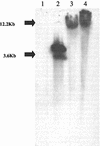
References
-
- Gales, A. C., and R. N. Jones. 2000. Antimicrobial activity and spectrum of the new glycylcycline, GAR-936 tested against 1,203 recent clinical isolates. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 36:19-36. - PubMed
-
- Hoellman, D. B., G. A. Pankuch, M. R. Jacobs, and P. A. Appelbaum. 2000. Antipneumococcal activities of GAR-936 (a new glycylcycline) compared to those of nine other agents against penicillin-susceptible and penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:1085-1088. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

