Prenatal diagnosis of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (4p-) in association with congenital hypospadias and foot deformity
- PMID: 12546710
- PMCID: PMC149368
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2393-3-1
Prenatal diagnosis of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (4p-) in association with congenital hypospadias and foot deformity
Abstract
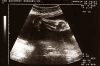
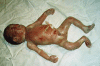
BACKGROUND: Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome is caused by distal deletion of the short arm of chromosome 4 (4p-). We report a case in which intrauterine growth restriction, hypospadias and foot deformity were detected by prenatal ultrasound examination at 29 weeks of gestation. CASE PRESENTATION: A 31-year-old gravida 2 partus 1 woman was referred at 29 weeks' gestation with suspicion of intrauterine growth restriction. Sonographic examination revealed deformity of the right lower limb and undescended testes with an irregular distal penis. A cordocentesis was performed and chromosome analysis revealed a 46,XY,del(4)(p14) karyotype. CONCLUSION: The prenatal detection of intrauterine growth restriction, hypospadias and foot deformity should lead doctors to suspect the presence of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
Figures

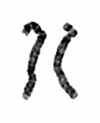
References
-
- Cooper H, Hirschhorn K. Apparent deletion of short arms of one chromosome (4 or 5) in a child with defects of midline fusion. Hum Chrom Newsl. 1961;4:14–16. - PubMed
-
- Verloes A, Schaaps JP, Herens C, Soyeur D, Hustin C, Dodinval P. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic hygroma and chorioangioma in the Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Prenat Diagn. 1991;11:129–132. - PubMed
-
- Lurie IW, Lazjuk GL, Ussova I, Presman EB, Gurevich DB. The Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. I. Genetics. Clin Genet. 1980;17:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Snijders RJ, Sherrod C, Gosden CM, Nicolaides KH. Fetal growth retardation associated malformations and chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;168:547–555. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

