Structural proton diffusion along lipid bilayers
- PMID: 12547784
- PMCID: PMC1302680
- DOI: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74919-4
Structural proton diffusion along lipid bilayers
Abstract
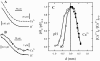
For H(+) transport between protein pumps, lateral diffusion along membrane surfaces represents the most efficient pathway. Along lipid bilayers, we measured a diffusion coefficient of 5.8 x 10(-5) cm(2) s(-1). It is too large to be accounted for by vehicle diffusion, considering proton transport by acid carriers. Such a speed of migration is accomplished only by the Grotthuss mechanism involving the chemical exchange of hydrogen nuclei between hydrogen-bonded water molecules on the membrane surface, and the subsequent reorganization of the hydrogen-bonded network. Reconstitution of H(+)-binding sites on the membrane surface decreased the velocity of H(+) diffusion. In the absence of immobile buffers, structural (Grotthuss) diffusion occurred over a distance of 100 micro m as shown by microelectrode aided measurements of the spatial proton distribution in the immediate membrane vicinity and spatially resolved fluorescence measurements of interfacial pH. The efficiency of the anomalously fast lateral diffusion decreased gradually with an increase in mobile buffer concentration suggesting that structural diffusion is physiologically important for distances of approximately 10 nm.
Figures

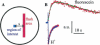
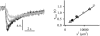
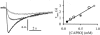
References
-
- Amman, D. 1986. Ion-Selective Microelectrodes. Principles, Design and Application. Springer, Berlin.
-
- Antonenko, Y. N., and A. A. Bulychev. 1991. Measurements of local pH changes near bilayer lipid membrane by means of a pH microelectrode and a protonophore-dependent membrane potential - comparison of the methods. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1070:279–282. - PubMed
-
- Antonenko, Y. N., O. N. Kovbasnjuk, and L. S. Yaguzhinsky. 1993. Evidence in favor of the existence of a kinetic barrier for proton transfer from a surface of bilayer phospholipid membrane to bulk water. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1150:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Antonenko, Y. N., and P. Pohl. 1998. Coupling of proton source and sink via H+-migration along the membrane surface as revealed by double patch-clamp experiments. FEBS Lett. 429:197–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

