Cell penetration and trafficking of polyomavirus
- PMID: 12552000
- PMCID: PMC141103
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2615-2622.2003
Cell penetration and trafficking of polyomavirus
Abstract
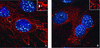
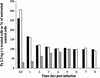
The murine polyomavirus (Py) enters mouse fibroblasts and kidney epithelial cells via an endocytic pathway that is caveola-independent (as well as clathrin-independent). In contrast, uptake of simian virus 40 into the same cells is dependent on caveola. Following the initial uptake of Py, both microtubules and microfilaments play roles in trafficking of the virus to the nucleus. Colcemid, which disrupts microtubules, inhibits the ability of Py to reach the nucleus and replicate. Paclitaxel, which stabilizes microtubules and prevents microtubule turnover, has no effect, indicating that intact but not dynamic microtubules are required for Py infectivity. Compounds that disrupt actin filaments enhance Py uptake while stabilization of actin filaments impedes Py infection. Virus particles are seen in association with actin in cells treated with microfilament-disrupting or filament-stabilizing agents at levels comparable to those in untreated cells, suggesting that a dynamic state of the microfilament system is important for Py infectivity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Uptake pathway of polyomavirus via ganglioside GD1a.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(22):12259-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.22.12259-12267.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15507613 Free PMC article.
-
Taxol-treated fibroblasts acquire an epithelioid shape and a circular pattern of actin bundles.Exp Cell Res. 1994 Jun;212(2):201-8. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1135. Exp Cell Res. 1994. PMID: 7910561
-
Involvement of cytoskeletal components in BK virus infectious entry.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(18):11734-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.18.11734-11741.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16140751 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubules in Polyomavirus Infection.Viruses. 2020 Jan 18;12(1):121. doi: 10.3390/v12010121. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 31963741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secrets of caveolae- and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis revealed by mammalian viruses.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1746(3):295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.06.009. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16126288 Review.
Cited by
-
Murine Polyomavirus Cell Surface Receptors Activate Distinct Signaling Pathways Required for Infection.mBio. 2016 Nov 1;7(6):e01836-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01836-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27803182 Free PMC article.
-
Transport of African swine fever virus from assembly sites to the plasma membrane is dependent on microtubules and conventional kinesin.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(15):7990-8001. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.15.7990-8001.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15254171 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolar endocytosis is critical for BK virus infection of human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(16):8552-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00924-07. Epub 2007 Jun 6. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17553887 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular trafficking pathway of BK Virus in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells.Virology. 2008 Feb 20;371(2):336-49. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.09.030. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Virology. 2008. PMID: 17976677 Free PMC article.
-
Infection of vero cells by BK virus is dependent on caveolae.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(21):11583-90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.21.11583-11590.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15479799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen, M., and T. Benjamin. 1997. Roles of N-glycans with α-2,6 as well as α-2,3 linked sialic acid in infection by polyoma virus. Virology 233:400-442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

