Kaposi's sarcoma-like tumors in a human herpesvirus 8 ORF74 transgenic mouse
- PMID: 12552002
- PMCID: PMC141078
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2631-2639.2003
Kaposi's sarcoma-like tumors in a human herpesvirus 8 ORF74 transgenic mouse
Abstract
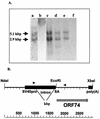
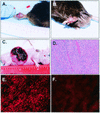
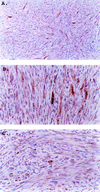
The product of human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) open reading frame 74 (ORF74) is related structurally and functionally to cellular chemokine receptors. ORF74 activates several cellular signaling pathways in the absence of added ligands, and NIH 3T3 cells expressing ORF74 are tumorigenic in nude mice. We have generated a line of transgenic (Tg) mice with ORF74 driven by the simian virus 40 early promoter. A minority (approximately 30%) of the Tg mice, including the founder, developed tumors resembling Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) lesions, which occurred most typically on the tail or legs. The tumors were highly vascularized, had a spindle cell component, expressed VEGF-C mRNA, and contained a majority of CD31(+) cells. CD31 and VEGF-C are typically expressed in KS. Tumors generally (but not always) occurred at single sites and most were relatively indolent, although several mice developed large visceral tumors. ORF74 was expressed in a minority of cells in the Tg tumors and in a few other tissues of mice with tumors; mice without tumors did not express detectable ORF74 in any tissues tested. Cell lines established from tumors expressed ORF74 in a majority of cells, expressed VEGF-C mRNA, and were tumorigenic in nude mice. The resultant tumors grew rapidly, metastasized, and continued to express ORF74. Cell lines established from these secondary tumors also expressed ORF74 and were tumorigenic. These data strongly suggest that ORF74 plays a role in the pathology of KS and confirm and extend previous findings on the tumorigenic potential of ORF74.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by the human herpesvirus 8 chemokine receptor ORF74: evidence for a paracrine model of Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8660-73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8660-8673.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507211 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of gene expression and a transactivation function exhibited by the vGCR (ORF74) chemokine receptor protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3421-39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3421-3439.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884567 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of murine herpesvirus 68- and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ORF74 G protein-coupled receptors by human and murine chemokines.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3343-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3343-3351.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016856 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV non-structural membrane proteins involved in the activation of intracellular signaling pathways and the pathogenesis of Kaposi's sarcoma.Curr Opin Virol. 2016 Oct;20:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Curr Opin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27518127 Review.
-
Initiation of angiogenic Kaposi's sarcoma lesions.Cancer Cell. 2003 Jan;3(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00002-3. Cancer Cell. 2003. PMID: 12559168 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BILF1 is a constitutively active G protein-coupled receptor.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):536-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.536-546.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596846 Free PMC article.
-
Endolysosomal trafficking of viral G protein-coupled receptor functions in innate immunity and control of viral oncogenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Mar 15;113(11):2994-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601860113. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26929373 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of mRNA Expression of ADGRD1/GPR133 and ADGRG7/GPR128 in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Lung Adenocarcinoma Calu-3 Cells.Cells. 2024 May 7;13(10):791. doi: 10.3390/cells13100791. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38786015 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cellular signaling by herpesvirus-encoded G protein-coupled receptors.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 9;6:40. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00040. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25805993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galpha protein selectivity determinant specified by a viral chemokine receptor-conserved region in the C tail of the human herpesvirus 8 g protein-coupled receptor.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2460-71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2460-2471.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14963144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ablashi, D., L. Chatlynne, H. Cooper, D. Thomas, M. Yadav, A. W. Norhanom, A. K. Chandana, V. Churdboonchart, S. A. R. Kulpradist, M. Patnaik, K. Liegmann, R. Masood, M. Reitz, F. Cleghorn, A. Manns, P. H. Levine, C. Rabkin, R. Biggar, F. Jensen, P. Gill, N. Jack, J. Edwards, J. Whitman, and C. Boshoff. 1999. Seroprevalence of human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) in countries of Southeast Asia compared to the USA, the Caribbean and Africa. Br. J. Cancer 81:893-897. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ariyoshi, K., M. S. van der Loeff, P. Cook, D. Whitby, T. Corrah, S. Jaffar, F. Cham, S. Sabally, D. O'Donovan, R. A. Weiss, T. F. Schulz, and H. Whittle. 1998. Kaposi's sarcoma in the Gambia, West Africa is less frequent in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 than in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection despite a high prevalence of human herpesvirus 8. J. Hum. Virol. 1:193-199. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis, L., E. Geras-Raaka, A. Varma, M. C. Gershengorn, and E. Cesarman. 1997. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature 385:347-350. - PubMed
-
- Bais, C., B. Santomasso, O. Coso, L. Arvanitakis, E. G. Raaka, J. S. Gutkind, A. S. Asch, E. Cesarman, M. C. Gershengorn, and E. A. Mesri. 1998. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature 391:86-89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

