E1A sensitizes cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha by downregulating c-FLIP S
- PMID: 12552004
- PMCID: PMC141118
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2651-2662.2003
E1A sensitizes cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha by downregulating c-FLIP S
Abstract
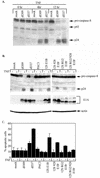
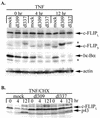
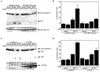
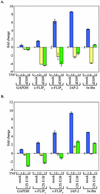
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) activates both apoptosis and NF-kappaB-dependent survival pathways, the former of which requires inhibition of gene expression to be manifested. c-FLIP is a TNF-alpha-induced gene that inhibits caspase-8 activation during TNF-alpha signaling. Adenovirus infection and E1A expression sensitize cells to TNF-alpha by allowing apoptosis in the absence of inhibitors of gene expression, suggesting that it may be disabling a survival signaling pathway. E1A promoted TNF-alpha-mediated activation of caspase-8, suggesting that sensitivity was occurring at the level of the death-inducing signaling complex. Furthermore, E1A expression downregulated c-FLIP(S) expression and prevented its induction by TNF-alpha. c-FLIP(S) and viral FLIP expression rescued E1A-mediated sensitization to TNF-alpha by restoring the resistance of caspase-8 to activation, thereby preventing cell death. E1A inhibited TNF-alpha-dependent induction of c-FLIP(S) mRNA and stimulated ubiquitination- and proteasome-dependent degradation of c-FLIP(S) protein. Since elevated c-FLIP levels confer resistance to apoptosis and promote tumorigenicity, interference with its induction by NF-kappaB and stimulation of its destruction in the proteasome may provide novel therapeutic approaches for facilitating the elimination of apoptosis-refractory tumor cells.
Figures
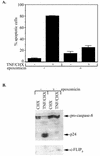
Similar articles
-
An inducible pathway for degradation of FLIP protein sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 21;277(25):22320-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202458200. Epub 2002 Apr 8. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11940602
-
Metabolic inhibitors sensitize for CD95 (APO-1/Fas)-induced apoptosis by down-regulating Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin 1-converting enzyme inhibitory protein expression.Cancer Res. 2000 Jul 15;60(14):3947-56. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10919673
-
Selective inhibition of FLICE-like inhibitory protein expression with small interfering RNA oligonucleotides is sufficient to sensitize tumor cells for TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Mol Med. 2002 Nov;8(11):725-32. Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12520089 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic signaling by TNFalpha: caspase activation and IkappaB degradation.Cytokine. 2003 Mar 21;21(6):286-94. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4666(03)00107-8. Cytokine. 2003. PMID: 12824002 Review.
-
The caspase-8 modulator c-FLIP.Crit Rev Immunol. 2005;25(1):31-58. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v25.i1.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15833082 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of tumor necrosis factor by microbial pathogens.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Feb;2(2):e4. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020004. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16518473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The androgen receptor directly targets the cellular Fas/FasL-associated death domain protein-like inhibitory protein gene to promote the androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jul;19(7):1792-802. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0445. Epub 2005 Feb 24. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15731171 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C virus core protein inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated apoptosis by a protective effect involving cellular FLICE inhibitory protein.J Virol. 2006 May;80(9):4372-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.9.4372-4379.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16611896 Free PMC article.
-
USP8 suppresses death receptor-mediated apoptosis by enhancing FLIPL stability.Oncogene. 2017 Jan 26;36(4):458-470. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.215. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27321185
-
Tumor suppressor BLU promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis by downregulating NF-κB signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 4;8(27):43853-43865. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14126. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28029652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkett, M., and T. D. Gilmore. 1999. Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6910-6924. - PubMed
-
- Bertin, J., R. C. Armstrong, S. Ottilie, M. D., Y. Wang, S. Banks, G. H. Wang, T. G. Senkevich, E. S. Alnemri, B. Moss, M. J. Lenardo, K. J. Tomaselli, and J. I. Cohen. 1997. Death effector domain-containing herpesvirus and poxvirus proteins inhibit both Fas- and TNFR-1-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:1172-1176. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, M. J., B. Holskin, J. Strickler, J. Gorniak, M. A. Clark, P. J. Johnson, M. Mitcho, and D. Shalloway. 1987. Induction by E1A oncogene expression of cellular susceptibility to lysis by TNF. Nature (London) 330:581-583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

