Molecular characterization of bovine enteric caliciviruses: a distinct third genogroup of noroviruses (Norwalk-like viruses) unlikely to be of risk to humans
- PMID: 12552024
- PMCID: PMC141104
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2789-2798.2003
Molecular characterization of bovine enteric caliciviruses: a distinct third genogroup of noroviruses (Norwalk-like viruses) unlikely to be of risk to humans
Abstract
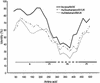
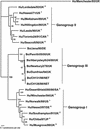
Bovine enteric caliciviruses (BoCVs) have been classified in the Norovirus (Norwalk-like virus) genus of the Caliciviridae, raising questions about zoonotic transmission and an animal reservoir for the human Norwalk-like viruses (NLVs), an important cause of nonbacterial gastroenteritis in humans. We examined the genetic relationship of human NLVs to BoCVs that were identified by using reverse transcription-PCR with primer pairs originally designed to detect human NLVs. Polymerase, capsid, and open reading frame 3 (ORF3) gene sequence analyses of BoCVs that were identified from 1976 to 2000 from throughout the United Kingdom showed that BoCVs formed a distinct third genogroup of closely related viruses distinct from the human genogroup I and II NLVs. Evidence was not obtained to support the concept that BoCVs are circulating in humans and pose a threat to human health.
Figures



References
-
- Ando, T., J. S. Noel, and R. L. Fankhauser. 2000. Genetic classification of “Norwalk-like viruses.” J. Infect. Dis. 181(Suppl. 2):S336-S348. - PubMed
-
- Berry, E. S., D. E. Skilling, J. E. Barlough, N. A. Vedros, L. J. Gage, and A. W. Smith. 1990. New marine calicivirus serotype infective for swine. Am. J. Vet. Res. 51:1184-1187. - PubMed
-
- Cauchi, M. R., J. C. Doultree, J. A. Marshall, and P. J. Wright. 1996. Molecular characterization of Camberwell virus and sequence variation in ORF3 of small round-structured (Norwalk-like) viruses. J. Med. Virol. 49:70-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

