Development of real-time PCR assays for the quantitative detection of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus, comparison of TaqMan probes, and molecular beacons
- PMID: 12552075
- PMCID: PMC1907370
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60446-1
Development of real-time PCR assays for the quantitative detection of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus, comparison of TaqMan probes, and molecular beacons
Abstract
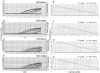
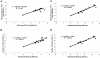
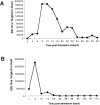
Human Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) can cause serious complications in immunocompromised patients. Rapid diagnosis of EBV and CMV infection is critical in the management of the disease so that anti-viral therapy can be started early. Here we describe the development of real-time PCR assays using TaqMan probes and molecular beacons and compare the performance of both assays with a well-established, validated, gel-based PCR method for the quantification of EBV and CMV in patients' samples. The TaqMan and molecular beacon assays were linear between 10 to 10(7) viral genomes/reaction. Both assays generated calibration curves with strong correlation and low intra-assay and interassay variation. Results of EBV and CMV viral load determination inpatient samples obtained by the gel-based and real-time PCR were very similar. The real-time PCR assays showed increases in viral load before clinical measures of viral disease and decreases in viral load during anti-viral therapy in two of six pediatric patients. The data indicate that these TaqMan and molecular beacon approaches are accurate, rapid, and reliable assays for the diagnosis and monitoring of EBV and CMV infections in patients.
Figures
References
-
- Bowen EF: Cytomegalovirus reactivation in patients infected with HIV: the use of polymerase chain reaction in prediction and management. Drugs 1999, 57:735-741 - PubMed
-
- Machida U, Kami M, Fukui T, Kazuyama Y, Kinoshita M, Tanaka Y, Kanda Y, Ogawa S, Honda H, Chiba S, Mitani K, Muto Y, Osumi K, Kimura S, Hirai H: Real-time automated PCR for early diagnosis and monitoring of cytomegalovirus infection after bone marrow transplantation. J Clin Microbiol 2000, 38:2536-2542 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orii T, Ohkohchi N, Kikuchi H, Koyamada N, Chubachi S, Satomi S, Kimura H, Hoshino Y, Morita M: Usefulness of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in following up patients with Epstein-Barr virus infection after liver transplantation. Clin Transpl 2000, 14:308-317 - PubMed
-
- Riddler SA, Breinig MC, McKnight JL: Increased levels of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected lymphocytes and decreased EBV nuclear antigen antibody responses are associated with the development of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid-organ transplant recipients. Blood 1994, 84:972-984 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

