Depletion of a single nucleoporin, Nup107, prevents the assembly of a subset of nucleoporins into the nuclear pore complex
- PMID: 12552102
- PMCID: PMC298712
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.252749899
Depletion of a single nucleoporin, Nup107, prevents the assembly of a subset of nucleoporins into the nuclear pore complex
Abstract
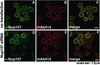
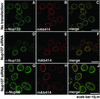
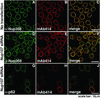
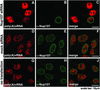
The nuclear pore complex (NPC) is a protein assembly that contains several distinct subcomplexes. The mammalian nucleoporin (Nup)-107 is part of a hetero-oligomeric complex, that also contains Nup160, Nup133, Nup96, and the mammalian homolog of yeast Sec13p. We used transfection of HeLa cells with small interfering RNAs to specifically deplete mRNA for Nup107. In a domino effect, Nup107 depletion caused codepletion of a subset of other Nups on their protein but not on their mRNA level. Among the affected Nups was a member of the Nup107 subcomplex, Nup133, whereas two other tested members of this complex, Nup96 and Sec13, were unaffected and assembled into Nup107Nup133-deficient NPCs. We also tested several phenylalanine-glycine repeat-containing Nups that serve as docking sites for karyopherins. Some of these, such as Nup358, Nup214 on the cytoplasmic, and Nup153 on the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC, failed to assemble into Nup107Nup133-depleted NPCs, whereas p62, a Nup at the center of the NPC, was unaffected. Interestingly, the filamentous, NPC-associated protein Tpr also failed to assemble into the NPCs of Nup107-depleted cells. These data indicate that Nup107 functions as a keystone Nup that is required for the assembly of a subset of Nups into the NPC. Despite the depletion of Nup107 and the accompanying effects on other Nups, there was no significant effect on the growth rate of these cells and only a partial inhibition of mRNA export. These data indicate redundancy of Nups in the function of the mammalian NPC.
Figures


References
-
- Allen T D, Cronshaw J M, Bagley S, Kiselewa E, Goldberg M W. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1651–1659. - PubMed
-
- Ryan K J, Wente S R. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12:361–371. - PubMed
-
- Rout M P, Aitchison J D. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16593–16596. - PubMed
-
- Vasu S K, Forbes D J. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:363–375. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Rout M P, Akey C W. Mol Cell. 1998;1:223–234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

