Lower blood glucose, hyperglucagonemia, and pancreatic alpha cell hyperplasia in glucagon receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 12552113
- PMCID: PMC298791
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0237106100
Lower blood glucose, hyperglucagonemia, and pancreatic alpha cell hyperplasia in glucagon receptor knockout mice
Abstract
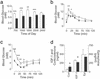
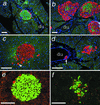
Glucagon, the counter-regulatory hormone to insulin, is secreted from pancreatic alpha cells in response to low blood glucose. To examine the role of glucagon in glucose homeostasis, mice were generated with a null mutation of the glucagon receptor (Gcgr(-/-)). These mice display lower blood glucose levels throughout the day and improved glucose tolerance but similar insulin levels compared with control animals. Gcgr(-/-) mice displayed supraphysiological glucagon levels associated with postnatal enlargement of the pancreas and hyperplasia of islets due predominantly to alpha cell, and to a lesser extent, delta cell proliferation. In addition, increased proglucagon expression and processing resulted in increased pancreatic glucogen-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) (1-37) and GLP-1 amide (1-36 amide) content and a 3- to 10-fold increase in circulating GLP-1 amide. Gcgr(-/-) mice also displayed reduced adiposity and leptin levels but normal body weight, food intake, and energy expenditure. These data indicate that glucagon is essential for maintenance of normal glycemia and postnatal regulation of islet and alpha and delta cell numbers. Furthermore, the lean phenotype of Gcgr(-/-) mice suggests glucagon action may be involved in the regulation of whole body composition.
Figures
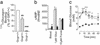
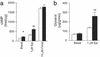
References
-
- Burcelin R, Katz E B, Charron M J. Diabetes Metab. 1996;22:373–396. - PubMed
-
- Lefèbvre P J. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:715–730. - PubMed
-
- Kieffer T J, Habener J F. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Porte D, Jr, Seeley R J, Woods S C, Baskin D G, Figlewicz D P, Schwartz M W. Diabetologia. 1998;41:863–881. - PubMed
-
- Holst J J. Regul Pept. 2000;93:45–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

