Course of illness, hippocampal function, and hippocampal volume in major depression
- PMID: 12552118
- PMCID: PMC298782
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0337481100
Course of illness, hippocampal function, and hippocampal volume in major depression
Abstract
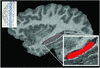
Studies have examined hippocampal function and volume in depressed subjects, but none have systematically compared never-treated first-episode patients with those who have had multiple episodes. We sought to compare hippocampal function, as assessed by performance on hippocampal-dependent recollection memory tests, and hippocampal volumes, as measured in a 1.5-T magnetic resonance imager, in depressed subjects experiencing a postpubertal onset of depression. Twenty never-treated depressed subjects in a first episode of depression were compared with matched healthy control subjects. Seventeen depressed subjects with multiple past episodes of depression were also compared with matched healthy controls and to the first-episode patients. Both first- and multiple-episode depressed groups had hippocampal dysfunction apparent on several tests of recollection memory; only depressed subjects with multiple depressive episodes had hippocampal volume reductions. Curve-fitting analysis revealed a significant logarithmic association between illness duration and hippocampal volume. Reductions in hippocampal volume may not antedate illness onset, but volume may decrease at the greatest rate in the early years after illness onset.
Figures
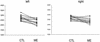
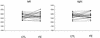
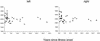
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

