Dentate gyrus volume is reduced before onset of plaque formation in PDAPP mice: a magnetic resonance microscopy and stereologic analysis
- PMID: 12552120
- PMCID: PMC298781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.242746599
Dentate gyrus volume is reduced before onset of plaque formation in PDAPP mice: a magnetic resonance microscopy and stereologic analysis
Abstract
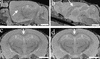
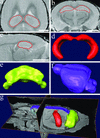
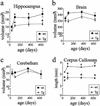
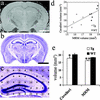
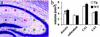
High-resolution magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) was used to determine regional brain volumetric changes in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. These transgenic (Tg) mice overexpress human mutant amyloid precursor protein (APP) V717F under control of platelet-derived growth factor promoter (PDAPP mice), and cortical and hippocampal beta-amyloid (Abeta) deposits accumulate in heterozygotes after 8-10 mos. We used MRM to obtain 3D volumetric data on mouse brains imaged in their skulls to define genotype- and age-related changes. Hippocampal, cerebellar, and brain volumes and corpus callosum length were quantified in 40-, 100-, 365-, and 630-day-old mice. Measurements taken at age 100 days, before Abeta deposition, revealed a 12.3% reduction of hippocampus volume in Tg mice compared with WT controls. This reduction persisted without progression to age 21 mos. A significant 18% increase in hippocampal volume occurred between 40 and 630 days in WT mice, and no corresponding significant increase occurred in Tg mice. Cavalieri volume estimates of hippocampal subfields from 100-day-old Tg mice further localized a 28% volume deficit in the dentate gyrus. In addition, corpus callosum length was reduced by approximately 25% in Tg mice at all ages analyzed. In summary, reduced hippocampal volume and corpus callosum length can be detected by MRM before Abeta deposition. We conclude that overexpression of APP and amyloid may initiate pathologic changes before the appearance of plaques, suggesting novel targets for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and further reinforcing the need for early diagnosis and treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe D. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Taylor J, Hardy J, Fischbeck K. Science. 2002;296:1991–1995. - PubMed
-
- Kuo Y M, Emmerling M R, Vigo-Pelfrey C, Kasunic T C, Kirkpatrick J B, Murdoch G H, Ball M J, Roher A E. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4077–4081. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt D R, Thinakaran G, Eckman C B, Lee M K, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada C M, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, et al. Neuron. 1996;17:1005–1013. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

