Eye opening induces a rapid dendritic localization of PSD-95 in central visual neurons
- PMID: 12552131
- PMCID: PMC298773
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0335785100
Eye opening induces a rapid dendritic localization of PSD-95 in central visual neurons
Abstract
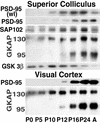
The membrane-associated guanylate kinase PSD-95 scaffolds N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors to cytoplasmic signaling molecules, and associates with other glutamate receptors at central synapses. However, regulation of PSD-95 in vivo is poorly understood. We provide evidence of an activity-dependent redistribution of PSD-95 to dendrites in central visual neurons that is tied to eye opening. Six hours after eye opening, increased dendritic PSD-95 coimmunoprecipitates with the same proportions of stargazin, increased proportions of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A, and decreased proportions of NR2B. Sustained high levels of PSD-95 in dendrites are dependent on continued pattern vision in juvenile but not mature animals, suggesting that the stabilization of PSD-95 at synapses may be involved in the control of developmental plasticity.
Figures



References
-
- Kornau H C, Schenker L T, Kennedy M B, Seeburg P H. Science. 1995;269:1737–1740. - PubMed
-
- Garcia E P, Mehta S, Blair L A, Wells D G, Shang J, Fukushima T, Fallon J R, Garner C C, Marshall J. Neuron. 1998;21:727–739. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Chetkovich D M, Petralia R S, Sweeney N T, Kawasaki Y, Wenthold R J, Bredt D S, Nicoll R A. Nature. 2000;408:936–943. - PubMed
-
- Husi H, Ward M A, Choudhary J S, Blackstock W P, Grant S G. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:661–669. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy M B. Science. 2000;290:750–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

