Evolutionary connection between the catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and the origin of RNA polymerases
- PMID: 12553882
- PMCID: PMC151600
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-3-1
Evolutionary connection between the catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and the origin of RNA polymerases
Abstract
Background: The eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RDRP) is involved in the amplification of regulatory microRNAs during post-transcriptional gene silencing. This enzyme is highly conserved in most eukaryotes but is missing in archaea and bacteria. No evolutionary relationship between RDRP and other polymerases has been reported so far, hence the origin of this eukaryote-specific polymerase remains a mystery.
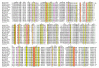
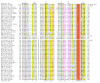
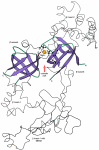
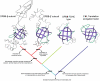
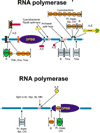
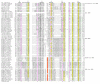
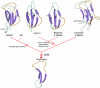
Results: Using extensive sequence profile searches, we identified bacteriophage homologs of the eukaryotic RDRP. The comparison of the eukaryotic RDRP and their homologs from bacteriophages led to the delineation of the conserved portion of these enzymes, which is predicted to harbor the catalytic site. Further, detailed sequence comparison, aided by examination of the crystal structure of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (DDRP), showed that the RDRP and the beta' subunit of DDRP (and its orthologs in archaea and eukaryotes) contain a conserved double-psi beta-barrel (DPBB) domain. This DPBB domain contains the signature motif DbDGD (b is a bulky residue), which is conserved in all RDRPs and DDRPs and contributes to catalysis via a coordinated divalent cation. Apart from the DPBB domain, no similarity was detected between RDRP and DDRP, which leaves open two scenarios for the origin of RDRP: i) RDRP evolved at the onset of the evolution of eukaryotes via a duplication of the DDRP beta' subunit followed by dramatic divergence that obliterated the sequence similarity outside the core catalytic domain and ii) the primordial RDRP, which consisted primarily of the DPBB domain, evolved from a common ancestor with the DDRP at a very early stage of evolution, during the RNA world era. The latter hypothesis implies that RDRP had been subsequently eliminated from cellular life forms and might have been reintroduced into the eukaryotic genomes through a bacteriophage. Sequence and structure analysis of the DDRP led to further insights into the evolution of RNA polymerases. In addition to the beta' subunit, beta subunit of DDRP also contains a DPBB domain, which is, however, distorted by large inserts and does not harbor a counterpart of the DbDGD motif. The DPBB domains of the two DDRP subunits together form the catalytic cleft, with the domain from the beta' subunit supplying the metal-coordinating DbDGD motif and the one from the beta subunit providing two lysine residues involved in catalysis. Given that the two DPBB domains of DDRP contribute completely different sets of active residues to the catalytic center, it is hypothesized that the ultimate ancestor of RNA polymerases functioned as a homodimer of a generic, RNA-binding DPBB domain. This ancestral protein probably did not have catalytic activity and served as a cofactor for a ribozyme RNA polymerase. Subsequent evolution of DDRP and RDRP involved accretion of distinct sets of additional domains. In the DDRPs, these included a RNA-binding Zn-ribbon, an AT-hook-like module and a sandwich-barrel hybrid motif (SBHM) domain. Further, lineage-specific accretion of SBHM domains and other, DDRP-specific domains is observed in bacterial DDRPs. In contrast, the orthologs of the beta' subunit in archaea and eukaryotes contains a four-stranded alpha + beta domain that is shared with the alpha-subunit of bacterial DDRP, eukaryotic DDRP subunit RBP11, translation factor eIF1 and type II topoisomerases. The additional domains of the RDRPs remain to be characterized.
Conclusions: Eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases share the catalytic double-psi beta-barrel domain, containing a signature metal-coordinating motif, with the universally conserved beta' subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Beyond this core catalytic domain, the two classes of RNA polymerases do not have common domains, suggesting early divergence from a common ancestor, with subsequent independent domain accretion. The beta-subunit of DDRP contains another, highly diverged DPBB domain. The presence of two distinct DPBB domains in two subunits of DDRP is compatible with the hypothesis that the ith the hypothesis that the ultimate ancestor of RNA polymerases was a RNA-binding DPBB domain that had no catalytic activity but rather functioned as a homodimeric cofactor for a ribozyme polymerase.
Figures

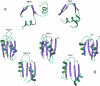
References
-
- Nelson DL, Cox MM. InLehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Worth Publishers Inc. 2000.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

