H+/ATP ratio of proton transport-coupled ATP synthesis and hydrolysis catalysed by CF0F1-liposomes
- PMID: 12554643
- PMCID: PMC140756
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg073
H+/ATP ratio of proton transport-coupled ATP synthesis and hydrolysis catalysed by CF0F1-liposomes
Abstract
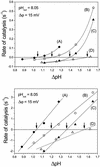
The H(+)/ATP ratio and the standard Gibbs free energy of ATP synthesis were determined with a new method using a chemiosmotic model system. The purified H(+)-translocating ATP synthase from chloroplasts was reconstituted into phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidic acid liposomes. During reconstitution, the internal phase was equilibrated with the reconstitution medium, and thereby the pH of the internal liposomal phase, pH(in), could be measured with a conventional glass electrode. The rates of ATP synthesis and hydrolysis were measured with the luciferin/luciferase assay after an acid-base transition at different [ATP]/([ADP][P(i)]) ratios as a function of deltapH, analysing the range from the ATP synthesis to the ATP hydrolysis direction and the deltapH at equilibrium, deltapH (eq) (zero net rate), was determined. The analysis of the [ATP]/([ADP][P(i)]) ratio as a function of deltapH (eq) and of the transmembrane electrochemical potential difference, delta micro approximately (H)(+) (eq), resulted in H(+)/ATP ratios of 3.9 +/- 0.2 at pH 8.45 and 4.0 +/- 0.3 at pH 8.05. The standard Gibbs free energies of ATP synthesis were determined to be 37 +/- 2 kJ/mol at pH 8.45 and 36 +/- 3 kJ/mol at pH 8.05.
Figures





References
-
- Böttcher B. and Gräber,P. (2000) The structure of the H+-ATP synthase from chloroplasts and its subcomplexes as revealed by electron microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1458, 404–416. - PubMed
-
- Boyer P.D. (1998) ATP synthase—past and future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1365, 3–9. - PubMed
-
- Davenport J.W. and McCarty,R.E. (1984) An analysis of proton fluxes coupled to electron transport and ATP synthesis in chloroplast thylakoids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 766, 363–374.
-
- Ferguson S.J. (2000) ATP synthase: what dictated the size of a ring? Curr. Biol., 10, R804–R808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

