The Helicobacter pylori CagA protein induces cortactin dephosphorylation and actin rearrangement by c-Src inactivation
- PMID: 12554652
- PMCID: PMC140734
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg050
The Helicobacter pylori CagA protein induces cortactin dephosphorylation and actin rearrangement by c-Src inactivation
Abstract
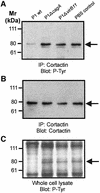
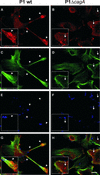
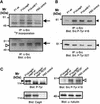
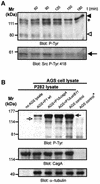
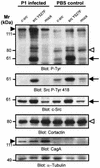
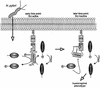
The gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori translocates the CagA protein into epithelial cells by a type IV secretion process. Translocated CagA is tyrosine phosphorylated (CagA(P-Tyr)) on specific EPIYA sequence repeats by Src family tyrosine kinases. Phos phorylation of CagA induces the dephosphorylation of as yet unidentified cellular proteins, rearrangements of the host cell actin cytoskeleton and cell scattering. We show here that CagA(P-Tyr) inhibits the catalytic activity of c-Src in vivo and in vitro. c-Src inactivation leads to tyrosine dephosphorylation of the actin binding protein cortactin. Concomitantly, cortactin is specifically redistributed to actin-rich cellular protrusions. c-Src inactivation and cortactin dephosphorylation are required for rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton. Moreover, CagA(P-Tyr)-mediated c-Src inhibition downregulates further CagA phosphorylation through a negative feedback loop. This is the first report of a bacterial virulence factor that inhibits signalling of a eukaryotic tyrosine kinase and on a role of c-Src inactivation in host cell cytoskeletal rearrangements.
Figures

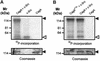

Similar articles
-
Role of Abl and Src family kinases in actin-cytoskeletal rearrangements induced by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;90(11):880-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.11.006. Epub 2011 Jan 17. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21247656 Review.
-
Activation of Abl by Helicobacter pylori: a novel kinase for CagA and crucial mediator of host cell scattering.Gastroenterology. 2007 Apr;132(4):1309-19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.01.050. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17408661
-
Interaction between the Helicobacter pylori CagA and alpha-Pix in gastric epithelial AGS cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Jan;1096:18-23. doi: 10.1196/annals.1397.065. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17405911
-
Influence of EPIYA-repeat polymorphism on the phosphorylation-dependent biological activity of Helicobacter pylori CagA.Gastroenterology. 2006 Apr;130(4):1181-90. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.038. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16618412
-
The versatility of Helicobacter pylori CagA effector protein functions: The master key hypothesis.Helicobacter. 2010 Jun;15(3):163-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2010.00759.x. Helicobacter. 2010. PMID: 20557357 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrin-mediated internalization of Staphylococcus aureus does not require vinculin.BMC Cell Biol. 2013 Jan 7;14:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-2. BMC Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23294665 Free PMC article.
-
Causal role of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jan 14;12(2):181-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.181. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16482615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in Helicobacter pylori-induced migration and invasive growth of gastric epithelial cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2011 Nov 1;9(1):27. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-9-27. Cell Commun Signal. 2011. PMID: 22044652 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the Helicobacter pylori plasticity region and cag pathogenicity island genes in the development of gastroduodenal diseases.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008 Nov;27(11):1053-9. doi: 10.1007/s10096-008-0549-8. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18560912
-
Cortactin Mediates Apoptosis of Gastric Epithelial Cells Induced by VacA Protein of Helicobacter pylori.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Jan;61(1):80-90. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3836-0. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26289258
References
-
- Akopyants N.S. et al. (1998) Analyses of the cag pathogenicity island of Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol., 28, 37–53. - PubMed
-
- Backert S., Ziska,E., Brinkmann,V., Zimny-Arndt,U., Fauconnier,A., Jungblut,P.R., Naumann,M. and Meyer,T.F. (2000) Translocation of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein in gastric epithelial cells by a type IV secretion apparatus. Cell Microbiol., 2, 155–164. - PubMed
-
- Backert S., Moese,S., Selbach,M., Brinkmann,V. and Meyer,T.F. (2001) Phosphorylation of tyrosine 972 of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein is essential for induction of a scattering phenotype in gastric epithelial cells. Mol. Microbiol., 42, 631–644. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

