Histone H1 enhances synergistic activation of the MMTV promoter in chromatin
- PMID: 12554659
- PMCID: PMC140736
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg052
Histone H1 enhances synergistic activation of the MMTV promoter in chromatin
Abstract
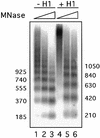
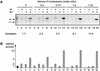
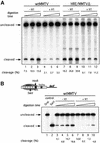
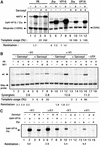
Minichromosomes assembled on the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter in vitro exhibit positioned nucleosomes, one of which covers the binding sites for progesterone receptor (PR) and nuclear factor 1 (NF1). Incorporation of histone H1 into MMTV minichromosomes improves the stability of this nucleosome and decreases basal transcription from the MMTV promoter, as well as its response to either PR or NF1. However, histone H1-containing minichromosomes display better PR binding and support a more efficient synergism between PR and NF1, leading to enhanced transcription initiation. A mutant MMTV promoter lacking positioned nucleosomes does not display enhanced transcriptional synergism in the presence of H1. Binding of PR leads to phosphorylation of H1, which leaves the promoter upon transcription initiation. Thus, H1 assumes a complex and dynamic role in the regulation of the MMTV promoter.
Figures
References
-
- Banks G.C., Deterding,L.J., Tomer,K.B. and Archer,T.K. (2001) Hormone-mediated dephosphorylation of specific histone H1 isoforms. J. Biol. Chem., 276, 36467–36473. - PubMed
-
- Bonte E. and Becker,P.B. (1999) Preparation of chromatin assembly extracts from preblastoderm Drosophila embryos. Methods Mol. Biol., 119, 187–194. - PubMed
-
- Bouvet P., Dimitrov,S. and Wolffe,A.P. (1994) Specific regulation of Xenopus chromosomal 5S rRNA gene transcription in vivo by histone H1. Genes Dev., 8, 1147–1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

