SMG-5, required for C.elegans nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, associates with SMG-2 and protein phosphatase 2A
- PMID: 12554664
- PMCID: PMC140740
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg056
SMG-5, required for C.elegans nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, associates with SMG-2 and protein phosphatase 2A
Abstract
mRNAs that contain premature stop codons are degraded selectively and rapidly in eukaryotes, a phenomenon termed 'nonsense-mediated mRNA decay' (NMD). We report here molecular analysis of smg-5, which encodes a novel protein required for NMD in Caenorhabditis elegans. Using a combination of immunoprecipitation and yeast two-hybrid assays, we identified a series of protein-protein interactions involving SMG-5. SMG-5 interacts with at least four proteins: (i) SMG-7, a previously identified protein required for NMD; (ii) SMG-2, a phosphorylated protein required for NMD in worms, yeasts and mammals; (iii) PR65, the structural subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A); and (iv) PP2A(C), the catalytic subunit of PP2A. Previous work demonstrated that both SMG-5 and SMG-7 are required for efficient dephosphorylation of SMG-2. Our results suggest that PP2A is the SMG-2 phosphatase, and the role of SMG-5 is to direct PP2A to its SMG-2 substrate. We discuss cycles of SMG-2 phosphorylation and their roles in NMD.
Figures

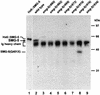



References
-
- Anderson P. (1995) Mutagenesis. Methods Cell Biol., 48, 31–58. - PubMed
-
- Aronoff R., Baran,R. and Hodgkin,J. (2001) Molecular identification of smg-4, required for mRNA surveillance in C.elegans. Gene, 268, 153–164. - PubMed
-
- Atkin A.L., Schenkman,L.R., Eastham,M., Dahlseid,J.N., Lelivelt,M.J. and Culbertson,M.R. (1997) Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 22163–22172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

