Imaging the localized protein interactions between Pit-1 and the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in the living pituitary cell nucleus
- PMID: 12554785
- PMCID: PMC2910340
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2002-0136
Imaging the localized protein interactions between Pit-1 and the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in the living pituitary cell nucleus
Abstract
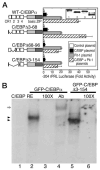
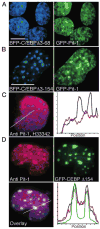
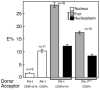
The homeodomain protein Pit-1 cooperates with the basic-leucine zipper protein CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) to control pituitary-specific prolactin gene transcription. We previously observed that C/EBPalpha was concentrated in regions of centromeric heterochromatin in pituitary GHFT1-5 cells and that coexpressed Pit-1 redistributed C/EBPalpha to the subnuclear sites occupied by Pit-1. Here, we used fluorescence resonance energy transfer microscopy to show that when C/EBPalpha was recruited by Pit-1, the average distance separating the fluorophores labeling the proteins was less than 7 nm. A mutation in the Pit-1 homeodomain, or truncation of the C/EBPalpha transactivation domain disrupted the redistribution of C/EBPalpha by Pit-1. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis revealed that the mutant Pit-1 still associated with C/EBPalpha, and the truncated C/EBPalpha still associated with Pit-1, but these interactions were preferentially localized in regions of centromeric heterochromatin. In contrast, a truncation in C/EBPalpha that prevented DNA binding also blocked its association with Pit-1, suggesting that the binding of C/EBPalpha to DNA is a critical first step in specifying its association with Pit-1. These findings indicated that the protein domains that specify the interaction of Pit-1 and C/EBPalpha are separable from the protein domains that direct the positioning of the associated proteins within the nucleus. The intimate association of Pit-1 and C/EBPalpha at certain sites within the living cell nucleus could foster their combinatorial activities in the regulation of pituitary-specific gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Gutierrez-Hartmann A. INSIGHT: Pit-1/GHF-1: a pituitary-specific transcription factor linking general signaling pathways to cell-specific gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1994;8:1447–1449. - PubMed
-
- Dasen JS, Rosenfeld MG. Combinatorial codes in signaling and synergy: lessons from pituitary development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:566–574. - PubMed
-
- Schaufele F. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α activation of the rat growth hormone promoter in pituitary progenitor GHFT1–5 cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:21484–21489. - PubMed
-
- Jacob KK, Stanley FM. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α is a physiological regulator of prolactin gene expression. Endocrinology. 1999;140:4542–4550. - PubMed
-
- Pombo A, Cuello P, Schul W, Yoon JB, Roeder RG, Cook PR, Murphy S. Regional and temporal specialization in the nucleus: a transcriptionally-active nuclear domain rich in PTF, Oct1 and PIKA antigens associates with specific chromosomes early in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1998;17:1768–1778. - PMC - PubMed

