Loss of HR6B ubiquitin-conjugating activity results in damaged synaptonemal complex structure and increased crossing-over frequency during the male meiotic prophase
- PMID: 12556476
- PMCID: PMC141135
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1151-1162.2003
Loss of HR6B ubiquitin-conjugating activity results in damaged synaptonemal complex structure and increased crossing-over frequency during the male meiotic prophase
Abstract
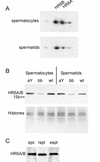
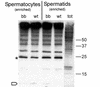
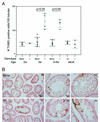
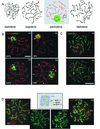
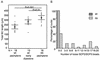
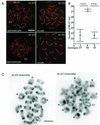
The ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes HR6A and HR6B are the two mammalian homologs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD6. In yeast, RAD6 plays an important role in postreplication DNA repair and in sporulation. HR6B knockout mice are viable, but spermatogenesis is markedly affected during postmeiotic steps, leading to male infertility. In the present study, increased apoptosis of HR6B knockout primary spermatocytes was detected during the first wave of spermatogenesis, indicating that HR6B performs a primary role during the meiotic prophase. Detailed analysis of HR6B knockout pachytene nuclei showed major changes in the synaptonemal complexes. These complexes were found to be longer. In addition, we often found depletion of synaptonemal complex proteins from near telomeric regions in the HR6B knockout pachytene nuclei. Finally, we detected an increased number of foci containing the mismatch DNA repair protein MLH1 in these nuclei, reflecting a remarkable and consistent increase (20 to 25%) in crossing-over frequency. The present findings reveal a specific requirement for the ubiquitin-conjugating activity of HR6B in relation to dynamic aspects of the synaptonemal complex and meiotic recombination in spermatocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Adams, M. D., S. E. Celniker, R. A. Holt, C. A. Evans, J. D. Gocayne, P. G. Amanatides, S. E. Scherer, P. W. Li, R. A. Hoskins, R. F. Galle, R. A. George, S. E. Lewis, S. Richards, M. Ashburner, S. N. Henderson, G. G. Sutton, J. R. Wortman, M. D. Yandell, Q. Zhang, L. X. Chen, R. C. Brandon, Y. H. Rogers, R. G. Blazej, M. Champe, B. D. Pfeiffer, K. H. Wan, C. Doyle, E. G. Baxter, G. Helt, C. R. Nelson, G. L. Gabor, J. F. Abril, A. Agbayani, H. J. An, C. Andrews-Pfannkoch, D. Baldwin, R. M. Ballew, A. Basu, J. Baxendale, L. Bayraktaroglu, E. M. Beasley, K. Y. Beeson, P. V. Benos, B. P. Berman, D. Bhandari, S. Bolshakov, D. Borkova, M. R. Botchan, J. Bouck, et al. 2000. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287:2185-2195. - PubMed
-
- Baarends, W. M., J. W. Hoogerbrugge, H. P. Roest, M. Ooms, J. Vreeburg, J. H. J. Hoeijmakers, and J. A. Grootegoed. 1999. Histone ubiquitination and chromatin remodeling in mouse spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 207:322-333. - PubMed
-
- Baarends, W. M., R. van der Laan, and J. A. Grootegoed. 2000. Specific aspects of the ubiquitin system in spermatogenesis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 23:597-604. - PubMed
-
- Baker, S. M., A. W. Plug, T. A. Prolla, C. E. Bronner, A. C. Harris, X. Yao, D. M. Christie, C. Monell, N. Arnheim, A. Bradley, T. Ashley, and R. M. Liskay. 1996. Involvement of mouse Mlh1 in DNA mismatch repair and meiotic crossing over. Nat. Genet. 13:336-342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
