Small Maf compound mutants display central nervous system neuronal degeneration, aberrant transcription, and Bach protein mislocalization coincident with myoclonus and abnormal startle response
- PMID: 12556477
- PMCID: PMC141134
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1163-1174.2003
Small Maf compound mutants display central nervous system neuronal degeneration, aberrant transcription, and Bach protein mislocalization coincident with myoclonus and abnormal startle response
Abstract
The small Maf proteins form heterodimers with CNC and Bach family proteins to elicit transcriptional responses from Maf recognition elements (MAREs). We previously reported germ line-targeted deficiencies in mafG plus mafK compound mutant mice. The most prominent mutant phenotype was a progressive maf dosage-dependent neuromuscular dysfunction. However, there has been no previous report regarding the effects of altered small-maf gene expression on neurological dysfunction. We show here that MafG and MafK are expressed in discrete central nervous system (CNS) neurons and that mafG::mafK compound mutants display neuronal degeneration coincident with surprisingly selective MARE-dependent transcriptional abnormalities. The CNS morphological changes are concurrent with the onset of a neurological disorder in the mutants, and the behavioral changes are accompanied by reduced glycine receptor subunit accumulation. Bach/small Maf heterodimers, which normally generate transcriptional repressors, were significantly underrepresented in nuclear extracts prepared from maf mutant brains, and Bach proteins fail to accumulate normally in nuclei. Thus compound mafG::mafK mutants develop age- and maf gene dosage-dependent cell-autonomous neuronal deficiencies that lead to profound neurological defects.
Figures
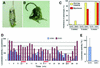

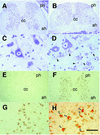
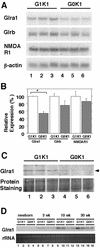
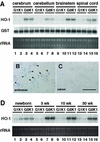

Similar articles
-
Perinatal synthetic lethality and hematopoietic defects in compound mafG::mafK mutant mice.EMBO J. 2000 Mar 15;19(6):1335-45. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.6.1335. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 10716933 Free PMC article.
-
Bach proteins belong to a novel family of BTB-basic leucine zipper transcription factors that interact with MafK and regulate transcription through the NF-E2 site.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;16(11):6083-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.11.6083. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8887638 Free PMC article.
-
Human small Maf proteins form heterodimers with CNC family transcription factors and recognize the NF-E2 motif.Oncogene. 1997 Apr 24;14(16):1901-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201024. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9150357
-
Small Maf proteins (MafF, MafG, MafK): History, structure and function.Gene. 2016 Jul 25;586(2):197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.058. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Gene. 2016. PMID: 27058431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The world according to Maf.Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Aug 1;25(15):2953-59. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.15.2953. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997. PMID: 9224592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf1 acts as a highly-conserved determinon for maintaining robust redox homeostasis in the eco-evo-devo process of life histories.Cell Stress. 2025 Jul 7;9:65-142. doi: 10.15698/cst2025.07.306. eCollection 2025. Cell Stress. 2025. PMID: 40703332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Joint profiling of histone modifications and transcriptome in single cells from mouse brain.Nat Methods. 2021 Mar;18(3):283-292. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01060-3. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 33589836 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of CXCL1 chemokine and CSF3 cytokine levels in myometrial cells by the MAFF transcription factor.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Apr;23(4):2517-2525. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14136. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30669188 Free PMC article.
-
The NRF2-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation of Antioxidant Defense Pathways: Relevance for Cell Type-Specific Vulnerability to Neurodegeneration and Therapeutic Intervention.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 21;11(1):8. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010008. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Biological Characteristics at the Peak of Cell Death in Different Hereditary Retinal Degeneration Mutants.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 29;12:728791. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.728791. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34777465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves-Rodrigues, A., L. Gregori, and M. E. Figueiredo-Pereira. 1998. Ubiquitin, cellular inclusions and their role in neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 21:516-520. - PubMed
-
- Blank, V., and N. C. Andrews. 1997. The Maf transcription factors: regulators of differentiation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22:437-441. - PubMed
-
- Dignam, J. D. 1990. Preparation of extracts from higher eukaryotes. Methods Enzymol. 182:194-203. - PubMed
-
- Farmer, S. C., C.-W. Sun, G. E. Winnier, B. L. M. Hogan, and T. M. Townes. 1997. The bZip transcription factor LCR-F1 is essential for mesoderm formation in mouse development. Genes Dev. 11:786-798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
