SKIP negatively regulates insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and membrane ruffle formation
- PMID: 12556481
- PMCID: PMC141139
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1209-1220.2003
SKIP negatively regulates insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and membrane ruffle formation
Abstract
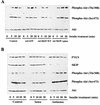
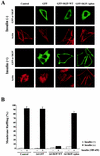
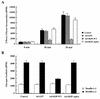
Skeletal muscle and kidney enriched inositol phosphatase (SKIP) is an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase that hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3] to downregulate intracellular levels. In this study, we show that SKIP inhibits phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in insulin-stimulated CHO cells. Ectopic expression of SKIP did not inhibit insulin-induced PI(3,4,5)P3 generation but did rapidly decrease insulin-induced intracellular PI(3,4,5)P3 levels compared with those in control cells. Further, insulin-induced phosphorylation of some downstream targets such as Akt and p70 S6 kinase was markedly inhibited by the ectopic expression of SKIP, whereas phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase was not. In contrast, downregulation of intracellular SKIP levels by antisense oligonucleotides dramatically enhanced Akt (protein kinase B) phosphorylation in response to insulin, suggesting that endogenous SKIP downregulates insulin signaling. SKIP also markedly inhibited GLUT4 translocation and membrane ruffle formation. We conclude that SKIP preferentially regulates glucose transport and actin cytoskeletal rearrangement among a variety of PI(3,4,5)P3 downstream events.
Figures




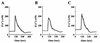

Similar articles
-
Regulation of insulin signaling and glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) exocytosis by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) phosphatase, skeletal muscle, and kidney enriched inositol polyphosphate phosphatase (SKIP).J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 2;287(10):6991-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.335539. Epub 2012 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22247557 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of SH2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 results in negative regulation of insulin-induced metabolic actions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via its 5'-phosphatase catalytic activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;21(5):1633-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.5.1633-1646.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238900 Free PMC article.
-
An SH2 domain-containing 5' inositolphosphatase inhibits insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and growth factor-induced actin filament rearrangement.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1081-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1081. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891043 Free PMC article.
-
Functional studies of the mammalian Sac1 phosphoinositide phosphatase.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2009;49(1):75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.01.006. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2009. PMID: 19534026 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The twentieth century struggle to decipher insulin signalling.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;7(11):867-73. doi: 10.1038/nrm2043. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17057754 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of insulin signaling by the phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate phosphatase SKIP through the scaffolding function of Pak1.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;32(17):3570-84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00636-12. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22751929 Free PMC article.
-
Sac3 is an insulin-regulated phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate phosphatase: gain in insulin responsiveness through Sac3 down-regulation in adipocytes.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):23961-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.025361. Epub 2009 Jul 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19578118 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Modulates Several Transcription-Factor Regulated Pathways in Mouse Skeletal Muscle Cells.Molecules. 2020 Nov 3;25(21):5098. doi: 10.3390/molecules25215098. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33153045 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN function: how normal cells control it and tumour cells lose it.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 15;382(Pt 1):1-11. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040825. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15193142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased insulin action in SKIP heterozygous knockout mice.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(17):5184-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01990-06. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18573875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiang, S.-H., A. C. Baumann, M. Kanzaki, C. D. Thurmond, T. R. Watson, L. C. Neudauer, G. I. Macara, E. J. Pessin, and R. A. Saltiel. 2000. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature 410:944-948. - PubMed
-
- Chung, J., T. C. Grammer, K. P. Lemon, A. Kazlauskas, and J. Blenis. 1994. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature 370:71-75. - PubMed
-
- Clement, S., U. Krause, F. Desmondt, J.-F. Tanti, J. Behrends, X. Pesesse, T. Sasaki, J. Penninger, M. Doherty, W. Malaisse, E. J. Dumont, L. Y. Marchand-Brustel, C. Erneux, L. Hue, and S. Schurmans. 2001. The lipid phosphatase SHIP2 controls insulin sensitivity. Nature 409:92-96. - PubMed
-
- Datta, S. R., A. Brunet, and M. E. Greenberg. 1999. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905-2927. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
