Inactivation of the nuclear receptor coactivator RAP250 in mice results in placental vascular dysfunction
- PMID: 12556486
- PMCID: PMC141133
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1260-1268.2003
Inactivation of the nuclear receptor coactivator RAP250 in mice results in placental vascular dysfunction
Abstract
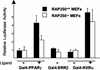
Coactivators constitute a diverse group of proteins that are essential for optimal transcriptional activity of nuclear receptors. In the past few years many coactivators have been identified but it is still unclear whether these proteins interact indiscriminately with all nuclear receptors and whether there is some redundancy in their functions. We have previously cloned and characterized RAP250 (ASC-2/PRIP/TRBP/NRC), an LXXLL-containing coactivator for nuclear receptors. In order to study its biological role, Rap250 null mice were generated by gene targeting. Here we show that genetic disruption of Rap250 results in embryonic lethality at embryonic day (E) 13.5. Histological examination of placentas revealed a dramatically reduced spongiotrophoblast layer, a collapse of blood vessels in the region bordering the spongiotrophoblast, and labyrinthine layers in placentas from Rap250(-/-) embryos. These findings suggest that the lethality of Rap250(-/-) embryos is the result of obstructed placental blood circulation. Moreover, the transcriptional activity of PPAR gamma is reduced in fibroblasts derived from Rap250(-/-) embryos, suggesting that RAP250 is an essential coactivator for this nuclear receptor in the placenta. Our results demonstrate that RAP250 is necessary for placental development and thus essential for embryonic development.
Figures








References
-
- Anzick, S. L., J. Kononen, R. L. Walker, D. O. Azorsa, M. M. Tanner, X. Y. Guan, G. Sauter, O. P. Kallioniemi, J. M. Trent, and P. S. Meltzer. 1997. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277:965-968. - PubMed
-
- Barak, Y., M. C. Nelson, E. S. Ong, Y. Z. Jones, P. Ruiz-Lozano, K. R. Chien, A. Koder, and R. M. Evans. 1999. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol. Cell 4:585-595. - PubMed
-
- Caira, F., P. Antonson, M. Pelto-Huikko, E. Treuter, and J.-Å. Gustafsson. 2000. Cloning and characterization of RAP250, a novel nuclear receptor coactivator. J. Biol. Chem. 275:5308-5317. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. W., R. J. Lin, R. L. Schiltz, D. Chakravarti, A. Nash, L. Nagy, M. L. Privalsky, Y. Nakatani, and R. M. Evans. 1997. Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300. Cell 90:569-580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
