Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2
- PMID: 12556489
- PMCID: PMC141149
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1292-1303.2003
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to the endoplasmic reticulum and promotes dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2
Abstract
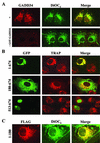
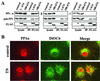
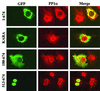
The growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein, GADD34, associates with protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) and promotes in vitro dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, (eIF-2 alpha). In this report, we show that the expression of human GADD34 in cultured cells reversed eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation induced by thapsigargin and tunicamycin, agents that promote protein unfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). GADD34 expression also reversed eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation induced by okadaic acid but not that induced by another phosphatase inhibitor, calyculin A (CA), which is a result consistent with PP1 being a component of the GADD34-assembled eIF-2 alpha phosphatase. Structure-function studies identified a bipartite C-terminal domain in GADD34 that encompassed a canonical PP1-binding motif, KVRF, and a novel RARA sequence, both of which were required for PP1 binding. N-terminal deletions of GADD34 established that while PP1 binding was necessary, it was not sufficient to promote eIF-2 alpha dephosphorylation in cells. Imaging of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-GADD34 proteins showed that the N-terminal 180 residues directed the localization of GADD34 at the ER and that GADD34 targeted the alpha isoform of PP1 to the ER. These data provide new insights into the mode of action of GADD34 in assembling an ER-associated eIF-2 alpha phosphatase that regulates protein translation in mammalian cells.
Figures




References
-
- Aggen, J. B., A. C. Nairn, and R. Chamberlin. 2000. Regulation of protein phosphatase-1. Chem. Biol. 7:R13-R23. - PubMed
-
- Babu, S. V., and K. V. Ramaiah. 1996. Type 1 phosphatase inhibitors reduce the restoration of guanine nucleotide exchange activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 2B inhibited reticulocyte lysates rescued by hemin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 327:201-208. - PubMed
-
- Bollen, M. 2001. Combinatorial control of protein phosphatase-1. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26:426-431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
