Snf1 kinases with different beta-subunit isoforms play distinct roles in regulating haploid invasive growth
- PMID: 12556493
- PMCID: PMC141157
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1341-1348.2003
Snf1 kinases with different beta-subunit isoforms play distinct roles in regulating haploid invasive growth
Abstract
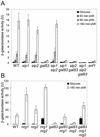
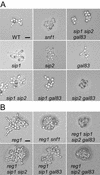
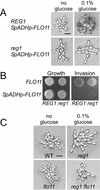
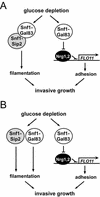
The Snf1 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been shown to have a role in regulating haploid invasive growth in response to glucose depletion. Cells contain three forms of the Snf1 kinase, each with a different beta-subunit isoform, either Gal83, Sip1, or Sip2. We present evidence that different Snf1 kinases play distinct roles in two aspects of invasive growth, namely, adherence to the agar substrate and filamentation. The Snf1-Gal83 form of the kinase is required for adherence, whereas either Snf1-Gal83 or Snf1-Sip2 is sufficient for filamentation. Genetic evidence indicates that Snf1-Gal83 affects adherence by antagonizing Nrg1- and Nrg2-mediated repression of the FLO11 flocculin and adhesin gene. In contrast, the mechanism(s) by which Snf1-Gal83 and Snf1-Sip2 affect filamentation is independent of FLO11. Thus, the Snf1 kinase regulates invasive growth by at least two distinct mechanisms.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pak1 protein kinase regulates activation and nuclear localization of Snf1-Gal83 protein kinase.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;24(18):8255-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8255-8263.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15340085 Free PMC article.
-
Snf1 protein kinase and the repressors Nrg1 and Nrg2 regulate FLO11, haploid invasive growth, and diploid pseudohyphal differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jun;22(12):3994-4000. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.3994-4000.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12024013 Free PMC article.
-
The beta-subunits of the Snf1 kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Gal83 and Sip2, but not Sip1, are redundant in glucose derepression and regulation of sterol biosynthesis.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Jul;77(2):371-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07209.x. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20545859
-
AMPK in Yeast: The SNF1 (Sucrose Non-fermenting 1) Protein Kinase Complex.Exp Suppl. 2016;107:353-374. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-43589-3_14. Exp Suppl. 2016. PMID: 27812987 Review.
-
Role of the yeast Snf1 protein kinase in invasive growth.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):175-7. doi: 10.1042/bst0310175. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546679 Review.
Cited by
-
Snf1/AMP-activated protein kinase activates Arf3p to promote invasive yeast growth via a non-canonical GEF domain.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 22;6:7840. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8840. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26198097 Free PMC article.
-
Neo-functionalization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a novel Nrg1-Rtg3 chimeric transcriptional modulator is essential to maintain mitochondrial DNA integrity.R Soc Open Sci. 2023 Nov 1;10(11):231209. doi: 10.1098/rsos.231209. eCollection 2023 Nov. R Soc Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 37920568 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of flocculation self-recognition in yeast and its role in mating and survival.mBio. 2015 Apr 14;6(2):e00427-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00427-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25873380 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006 Mar;70(1):253-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.70.1.253-282.2006. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16524925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor Nrg1 mediates capsule formation, stress response, and pathogenesis in Cryptococcus neoformans.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Jul;5(7):1147-56. doi: 10.1128/EC.00145-06. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16835458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
