Maintenance of open chromatin and selective genomic occupancy at the cell cycle-regulated histone H4 promoter during differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells
- PMID: 12556504
- PMCID: PMC141140
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1460-1469.2003
Maintenance of open chromatin and selective genomic occupancy at the cell cycle-regulated histone H4 promoter during differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells
Abstract
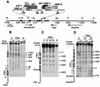
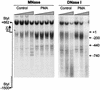
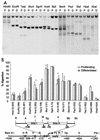
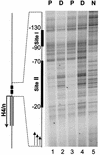
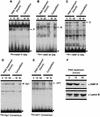
During the shutdown of proliferation and onset of differentiation of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells, expression of the cell cycle-dependent histone genes is downregulated at the level of transcription. To address the mechanism by which this regulation occurs, we examined the chromatin structure of the histone H4/n (FO108, H4FN) gene locus. Micrococcal nuclease, DNase I, and restriction enzymes show similar cleavage sites and levels of sensitivity at the H4/n locus in both proliferating and differentiated HL-60 cells. In contrast, differentiation-related activation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21(cip1/WAF1) gene is accompanied by increased nuclease hypersensitivity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays of the H4/n gene reveal that acetylated histones H3 and H4 are maintained at the same levels in proliferating and postproliferative cells. Thus, the chromatin of the H4/n locus remains in an open state even after transcription ceases. Using ligation-mediated PCR to visualize genomic DNase I footprints at single-nucleotide resolution, we find that protein occupancy at the site II cell cycle element is selectively diminished in differentiated cells while the site I element remains occupied. Decreased occupancy of site II is reflected by loss of the site II binding protein HiNF-P. We conclude that H4 gene transcription during differentiation is downregulated by modulating protein interaction at the site II cell cycle element and that retention of an open chromatin conformation may be associated with site I occupancy.
Figures
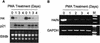



References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1997. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Aziz, F., A. J. van Wijnen, P. S. Vaughan, S. Wu, A. R. Shakoori, J. B. Lian, K. J. Soprano, J. L. Stein, and G. S. Stein. 1998. The integrated activities of IRF-2 (HiNF-M) CDP/cut (HiNF-D) and H4TF-2 (HiNF-P) regulate transcription of a cell cycle controlled human histone H4 gene: mechanistic differences between distinct H4 genes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 25:1-12. - PubMed
-
- Baumbach, L. L., G. S. Stein, and J. L. Stein. 1987. Regulation of human histone gene expression: transcriptional and posttranscriptional control in the coupling of histone messenger RNA stability with DNA replication. Biochemistry 26:6178-6187. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum, M. J., K. L. Wright, A. J. van Wijnen, A. L. Ramsey-Ewing, M. T. Bourke, T. J. Last, F. Aziz, B. Frenkel, B. R. Rao, N. Aronin, G. S. Stein, and J. L. Stein. 1995. Functional role for Sp1 in the transcriptional amplification of a cell cycle regulated histone H4 gene. Biochemistry 34:7648-7658. - PubMed
-
- Bulger, M., and M. Groudine. 1999. Looping versus linking: toward a model for long-distance gene activation. Genes Dev. 13:2465-2477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
