Current applications and future direction of MR mammography
- PMID: 12556951
- PMCID: PMC2376788
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600713
Current applications and future direction of MR mammography
Abstract
Compared with triple assessment for symptomatic and occult breast disease, magnetic resonance mammography (MRM) offers higher sensitivity for the detection of multifocal cancer, which is important in selecting patients appropriately for breast-conserving surgery. It is an ideal tool for the screening of patients with a high risk of breast cancer or where there is axillary disease or nipple discharge and conventional imaging has not revealed the primary focus. Techniques are now available to biopsy lesions only apparent on MRM. MRM can differentiate scar tissue from tumour; therefore, it is useful in patients in which there is possible recurrent disease. Clinical and X-ray mammographic assessment of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy may be unreliable because of replacement of the tumour with scar tissue. MRM can identify responders and nonresponders with more accuracy. It is the modality of choice for the assessment of breast implants for rupture with accuracy higher than X-ray mammography and ultrasound. Advances in both spatial and temporal resolutions, the imaging sequences employed, pharmacokinetic modelling of contrast uptake, the use of dedicated and now phased-array breast coils, and gadolinium-based contrast agents have all played their part in the advancement of this imaging technique. Despite the limitations of patient compliance, scan-time and cost, this review describes how MRM has become a valuable tool in breast disease, especially in cases of diagnostic uncertainty. However, MRM must make the transition from research institutions into routine clinical practice.
Figures

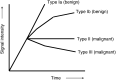


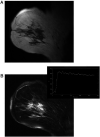

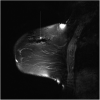
Comment in
-
Improved safety and effectiveness of imaging predicted for MR mammography.Br J Cancer. 2004 Jan 12;90(1):278-9; author reply 280. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601442. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14710240 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
3D-MR mammography-guided breast conserving surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: clinical results and future perspectives with reference to FDG-PET.Breast Cancer. 2001;8(4):351-4. doi: 10.1007/BF02967536. Breast Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11791129 Clinical Trial.
-
[Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of breast diseases].Orv Hetil. 2001 Sep 30;142(39):2123-31. Orv Hetil. 2001. PMID: 11723831 Hungarian.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: potential for lesion characterization.J BUON. 2004 Jan-Mar;9(1):77-82. J BUON. 2004. PMID: 17385833
-
[Modern diagnostics of the breast].Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1993 Jan;53(1):1-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1023629. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1993. PMID: 8382649 Review. German.
-
Breast MR imaging: current indications and advanced imaging techniques.Radiol Clin North Am. 2010 Sep;48(5):1013-42. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.06.011. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010. PMID: 20868898 Review.
Cited by
-
A high spatial resolution 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging technique for breast cancer with a short echo time.Magn Reson Imaging. 2008 Apr;26(3):360-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. PMID: 17904326 Free PMC article.
-
[Oncologic screening with whole-body MRI: possibilities and limitations].Radiologe. 2004 Sep;44(9):854-63. doi: 10.1007/s00117-004-1104-y. Radiologe. 2004. PMID: 15349733 Review. German.
-
Breast tomosynthesis in clinical practice: initial results.Eur Radiol. 2010 Jan;20(1):16-24. doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1523-2. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Eur Radiol. 2010. PMID: 19657655
-
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Preoperative Staging and Work-Up of Patients Affected by Invasive Lobular Carcinoma or Invasive Ductolobular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jun 26;2018:1569060. doi: 10.1155/2018/1569060. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30046588 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of breast tumors using diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI).PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e113240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113240. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25406010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beahrs OH, Henson DE, Hunter RVP, Kennedy BJ (1992) AJCC manual for staging of cancer. 4th edn. Philadelphia: Lippicott, 1992
-
- Belli P, Costantini M, Romani M, Marano P, Pastore G (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging in breast cancer recurrence. Breast Cancer Res Treat 73: 223–235 - PubMed
-
- Bradley AJ, Carrington BM, Hammond CL, Swindell R, Magee B (2000) accuracy of axillary MR imaging in treated breast cancer for distinguishing between recurrent tumour and treatment effects: does intravenous Gd–DTPA enhancement help in cases of diagnostic dilemma. Clin Radiol 55: 921–928 - PubMed
-
- Brown J, Buckley D, Coulthard A, Dixon AK, Dixon JM (2000) Magnetic resonance imaging screening in women at genetic risk of breast cancer: imaging and analysis protocol for the UK multi-centre study. Magn Reson Imag 18: 765–776 - PubMed
-
- Buckley DL, Drew PJ, Mussurakis S, Monson JRT, Horsman A (1997) Microvessel density in invasive breast cancer assessed by dynamic Gd–DTPA enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imag 7: 461–464 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

