NF-kappaB inhibition impairs the radioresponse of hypoxic EMT-6 tumour cells through downregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 12556970
- PMCID: PMC2376775
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600678
NF-kappaB inhibition impairs the radioresponse of hypoxic EMT-6 tumour cells through downregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
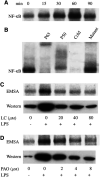
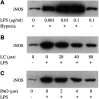
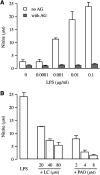
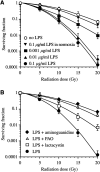
Hypoxic EMT-6 tumour cells displayed a high level of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and an increased radiosensitivity after a 16 h exposure to lipopolysaccharide, a known activator of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Both iNOS activation and radioresponse were impaired by the NF-kappaB inhibitors phenylarsine oxide and lactacystin. Contrasting to other studies, our data show that inhibition of NF-kappaB may impair the radioresponse of tumour cells through downregulation of iNOS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inducible nitric-oxide synthase is regulated by the proteasome degradation pathway.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 29;276(26):24268-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100725200. Epub 2001 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11312270
-
Lipid a radiosensitizes hypoxic EMT-6 tumor cells: role of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Nov 1;57(3):779-86. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00662-x. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 14529784
-
Inhibition of NF-kappaB by IkappaB prevents cytokine-induced NO production and promotes enterocyte apoptosis in vitro.Shock. 2000 Sep;14(3):366-73. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200014030-00022. Shock. 2000. PMID: 11028558
-
Hypoxic tumor cell radiosensitization: role of the iNOS/NO pathway.Bull Cancer. 2008 Mar;95(3):282-91. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2008.0592. Bull Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18390408 Review.
-
Blockade of NF-kappaB activation and donation of nitric oxide: new treatment options in inflammatory bowel disease?Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2002;(236):37-41. doi: 10.1080/003655202320621436. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 2002. PMID: 12408502 Review.
Cited by
-
β-Elemene enhances radiosensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell traits via Prx-1/NF-kB/iNOS signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 9;13(2):2575-2592. doi: 10.18632/aging.202291. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33316778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambs S, Merriam WG, Bennett WP, Felley-Bosco E, Ogunfusika MO, Oser SM, Klein S, Shields PG, Billiar TR, Harris CC (1998) Frequent nitric oxide synthase-2 expression in human colon adenomas: implication for tumor angiogenesis and colon cancer progression. Cancer Res 58: ;334–341 - PubMed
-
- Bradbury CM, Markovina S, Wei SJ, Rene LM, Zoberi I, Horikoshi N, Gius D (2001) Indomethacin-induced radiosensitization and inhibition of ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation in HeLa cells occur via a mechanism involving p38 MAP kinase. Cancer Res 61: 7689–7696 - PubMed
-
- Elliott PJ, Ross JS (2001) The proteasome: a new target for novel drug therapies. Am J Clin Pathol 116: 637–646 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

