Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel cold-adapted chitinase (ChiB) from a marine bacterium, Alteromonas sp. strain O-7
- PMID: 12562783
- PMCID: PMC142845
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1153-1160.2003
Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel cold-adapted chitinase (ChiB) from a marine bacterium, Alteromonas sp. strain O-7
Abstract
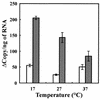
The chitinase B (ChiB) secreted by Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 was purified, and the corresponding gene (chiB) was cloned and sequenced. The open reading frame of the chiB gene encodes a protein of 850 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 90,223 Da. ChiB is a modular enzyme consisting of two reiterated domains and a catalytic domain belonging to chitinase family 18. The reiterated domains are composed of chitin-binding domain (ChtBD) type 3 and two fibronectin type III (Fn3)-like domains. Expression plasmids coding for ChiB or deletion derivatives thereof were constructed in Escherichia coli. Deletion analysis showed that the ChtBD of ChiB plays an important role in efficient hydrolysis of insoluble chitin. The optimum pH and temperature of ChiB were 6.0 and 30 degrees C, respectively. The enzyme showed relatively high catalysis, even at low temperatures close to 0 degrees C, and remarkable thermal lability compared to ChiA and ChiC, which are the mesophilic chitinases of the same strain. The kca)/Km value for the ChiB reaction at 10 degrees C was about 4.7 times higher than that of ChiC. These results suggest that ChiB is a cold-adapted enzyme. The RNA transcript of chiB was induced by 1% GlcNAc, and along with a rise in temperature, the RNA transcript showed a tendency to decrease. Thus, among the ChiA, ChiB, and ChiC chitinases, production of ChiB may be advantageous for the strain, allowing it to easily acquire nutrients from chitin and to survive in cold environments.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of the gene cluster involved in chitin degradation in a marine bacterium, Alteromonas sp. strain O-7.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002 Jan;68(1):263-70. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.1.263-270.2002. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11772635 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of four chitinases (chia, chib, chic, and chid) in the chitin degradation system of marine bacterium Alteromonas sp. strain O-7.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Apr;71(4):1811-5. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.4.1811-1815.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15812005 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of chitinase genes from an alkaliphilic actinomycete, Nocardiopsis prasina OPC-131.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Feb;69(2):894-900. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.2.894-900.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12571009 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene encoding Clostridium paraputrificum chitinase ChiB and analysis of the functions of novel cadherin-like domains and a chitin-binding domain.J Bacteriol. 1997 Dec;179(23):7306-14. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.23.7306-7314.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9393694 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the gene encoding a novel chitin-binding protease from Alteromonas sp. strain O-7 and its role in the chitinolytic system.J Bacteriol. 2002 Apr;184(7):1865-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1865-1872.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11889092 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cloning, characterization and expression of the chitinase gene of Enterobacter sp. NRG4.Indian J Microbiol. 2008 Sep;48(3):358-64. doi: 10.1007/s12088-008-0044-z. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Indian J Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 23100735 Free PMC article.
-
The stability of the TIM-barrel domain of a psychrophilic chitinase.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015 Jul 30;3:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2015.07.016. eCollection 2015 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2015. PMID: 29124173 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics, Proteomics, and Antifungal Activity of Chitinase from the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Curtobacterium sp. CBMAI 2942.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 26;25(17):9250. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179250. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273199 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning of Beauveria bassiana chitinase gene Bbchit1 and its application to improve fungal strain virulence.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jan;71(1):363-70. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.363-370.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15640210 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning, expression and biochemical characterisation of a cold-adapted novel recombinant chitinase from Glaciozyma antarctica PI12.Microb Cell Fact. 2011 Nov 4;10:94. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-94. Microb Cell Fact. 2011. PMID: 22050784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghajari, N., G. Feller, C. Gerday, and R. Haser. 1998. Structures of the psychrophilic Alteromonas haloplanktis α-amylase give insights into cold adaptation at a molecular level. Structure 6:1503-1516. - PubMed
-
- Aittaleb, M., R. Hubner, J. Lamotte-Brasseur, and C. Gerday. 1997. Cold adaptation parameters derived from cDNA sequencing and molecular modeling of elastase from Antarctic fish Notothenia neglecta. Protein Eng. 10:475-477. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, M., J. P. Zeelen, V. Mainfroid, F. Rentier-Delrue, J. A. Martia, L. Wyns, R. K. Wierenga, and D. Maes. 1998. Triose-phosphate isomerase (TIM) of the psychrophilic bacterium Vibrio marinus: kinetic and structural properties. J. Biol. Chem. 273:2199-2206. - PubMed
-
- Argos, P., M. G. Rossman, U. M. Grau, H. Zuber, G. Frank, and J. D. Tratschin. 1979. Thermal stability and protein structure. Biochemistry. 18:5698-5703. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the peptide of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

