Analysis of DNA binding and transcriptional activation by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR of Xanthobacter flavus
- PMID: 12562794
- PMCID: PMC142840
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1245-1252.2003
Analysis of DNA binding and transcriptional activation by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR of Xanthobacter flavus
Abstract
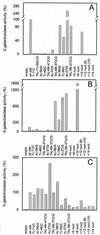
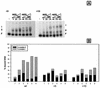
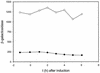
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR controls the expression of the cbb and gap-pgk operons in Xanthobacter flavus, which encode the majority of the enzymes of the Calvin cycle required for autotrophic CO2 fixation. The cbb operon promoter of this chemoautotrophic bacterium contains three potential CbbR binding sites, two of which partially overlap. Site-directed mutagenesis and subsequent analysis of DNA binding by CbbR and cbb promoter activity were used to show that the potential CbbR binding sequences are functional. Inverted repeat IR1 is a high-affinity CbbR binding site. The main function of this repeat is to recruit CbbR to the cbb operon promoter. In addition, it is required for negative autoregulation of cbbR expression. IR3 represents the main low-affinity binding site of CbbR. Binding to IR3 occurs in a cooperative manner, since mutations preventing the binding of CbbR to IR1 also prevent binding to the low-affinity site. Although mutations in IR3 have a negative effect on the binding of CbbR to this site, they result in an increased promoter activity. This is most likely due to steric hindrance of RNA polymerase by CbbR since IR3 partially overlaps with the -35 region of the cbb operon promoter. Mutations in IR2 do not affect the DNA binding of CbbR in vitro but have a severe negative effect on the activity of the cbb operon promoter. This IR2 binding site is therefore critical for transcriptional activation by CbbR.
Figures
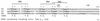



Similar articles
-
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator CbbR controlling autotrophic CO2 fixation by Xanthobacter flavus is an NADPH sensor.J Bacteriol. 1998 Mar;180(6):1411-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.6.1411-1417.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9515907 Free PMC article.
-
Operator binding of the CbbR protein, which activates the duplicate cbb CO2 assimilation operons of Alcaligenes eutrophus.J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(22):6568-74. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.22.6568-6574.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7592435 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid substitutions in the transcriptional regulator CbbR lead to constitutively active CbbR proteins that elevate expression of the cbb CO2 fixation operons in Ralstonia eutropha (Cupriavidus necator) and identify regions of CbbR necessary for gene activation.Microbiology (Reading). 2015 Sep;161(9):1816-1829. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000131. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Microbiology (Reading). 2015. PMID: 26296349
-
Genetics and control of CO(2) assimilation in the chemoautotroph Ralstonia eutropha.Arch Microbiol. 2002 Aug;178(2):85-93. doi: 10.1007/s00203-002-0441-3. Epub 2002 Jun 14. Arch Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12115053 Review.
-
CbbR, the Master Regulator for Microbial Carbon Dioxide Fixation.J Bacteriol. 2015 Nov;197(22):3488-98. doi: 10.1128/JB.00442-15. Epub 2015 Aug 31. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26324454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling RubisCO Form I and Form II Regulation in an Uncultured Organism from a Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent via Metagenomic and Mutagenesis Studies.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jul 12;8:1303. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01303. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28747908 Free PMC article.
-
Autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle by the denitrifying methanotroph "Candidatus Methylomirabilis oxyfera".Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Apr;80(8):2451-60. doi: 10.1128/AEM.04199-13. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24509918 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of organic sulfur compound utilisation in Advenella mimigardefordensis strain DPN7T.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174256. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358882 Free PMC article.
-
Three of four GlnR binding sites are essential for GlnR-mediated activation of transcription of the Amycolatopsis mediterranei nas operon.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(11):2595-602. doi: 10.1128/JB.00182-13. Epub 2013 Mar 29. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23543714 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating mechanism involves internal sensing of NADP+ and α-ketogutarate levels by transcription factor CcmR.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41286. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041286. Epub 2012 Jul 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Gibson, J. L., and F. R. Tabita. 1977. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J. Biol. Chem. 252:943-949. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

