Role of two novel two-component regulatory systems in development and phosphatase expression in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 12562808
- PMCID: PMC142856
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1376-1383.2003
Role of two novel two-component regulatory systems in development and phosphatase expression in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
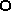
We have cloned a two-component regulatory system (phoR2-phoP2) of Myxococcus xanthus while searching for genes that encode proteins with phosphatase activity, where phoR2 encodes the histidine kinase and phoP2 encodes the response regulator. A second system, phoR3-phoP3, was identified and isolated by using phoP2 as a probe. These two systems are quite similar, sharing identities along the full-length proteins of 52% on the histidine kinases and 64% on the response regulators. The predicted structures of both kinases suggest that they are anchored to the membrane, with the sensor domains being located in the periplasmic space and the kinase domains in the cytoplasm. The response regulators (PhoP2 and PhoP3) exhibit a helix-loop-helix motif typical of DNA-binding proteins in the effector domains located in the C-terminal region. Studies on two single-deletion mutants and one double-deletion mutant have revealed that these systems are involved in development. Mutant fruiting bodies are not well packed, originating loose and flat aggregates where some myxospores do not reshape properly, and they remain as elongated cells. These systems are also involved in the expression of Mg-independent acid and neutral phosphatases, which are expressed during development. The neutral phosphatase gene is especially dependent on PhoP3. Neither PhoP2 nor PhoP3 regulates the expression of alkaline phosphatases and the pph1 gene.
Figures


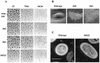
 , amino acids that constitute the two helixes of the helix-loop-helix motif.
, amino acids that constitute the two helixes of the helix-loop-helix motif.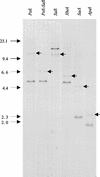
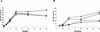
References
-
- Avery, L., and D. Kaiser. 1983. In situ transposon replacement and isolation of a spontaneous tandem duplication. Mol. Gen. Genet. 19:99-109. - PubMed
-
- Bilwes, A. M., L. A. Alex, B. R. Crane, and M. I. Simon. 1999. Structure of CheA, a signal-transducing histidine kinase. Cell 96:131-141. - PubMed
-
- Capela, D., F. Barloy-Hubler, J. Gouzy, G. Bothe, F. Ampe, J. Batut, P. Boistard, A. Becker, M. Boutry, E. Cadieu, S. Dreano, S. Gloux, T. Godrie, A. Goffeau, D. Kahn, E. Kiss, V. Lelaure, D. Masuy, T. Pohl, D. Portetelle, A. Puehler, B. Purnelle, U. Ramsperger, C. Renard, P. Thebault, M. Vandenbol, S. Weidner, and F. Galibert. 2001. Analysis of the chromosome sequence of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:9877-9882. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

