Mouse muscle denervation increases expression of an alpha7 nicotinic receptor with unusual pharmacology
- PMID: 12562921
- PMCID: PMC2342616
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.036368
Mouse muscle denervation increases expression of an alpha7 nicotinic receptor with unusual pharmacology
Abstract
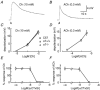
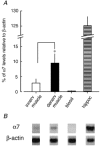
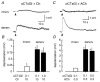
Neuronal nicotinic alpha7 subunits have been found in chick and rat skeletal muscle during development and denervation. In the present study, reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to detect alpha7 subunit mRNA in denervated mouse muscle. To determine whether the alpha7 subunit forms functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in muscle, choline was used to induce a membrane depolarization because choline has been considered a specific agonist of alpha7-containing (alpha7*) nAChRs. We found, however, that choline (3-10 mM) also weakly activates muscle nAChRs. After inhibiting muscle nAChRs with a specific muscle nAChR inhibitor, alpha-conotoxin GI (alphaCTxGI), choline was used to activate the alpha7* nAChRs on muscle selectively. Four weeks after denervation, rapid application of choline (10 mM) elicited a substantial depolarization in the presence of alphaCTxGI (0.1 microM). This component of the depolarization was never present in denervated muscles obtained from mutant mice lacking the alpha7 subunit (i.e. alpha7-null mice). The depolarization component that is resistant to alphaCTxGI was antagonized by pancuronium (3-10 microM) and by a 4-oxystilbene derivative (F3, 0.1-0.5 microM) at concentrations considered highly specific for alpha7* nAChRs. Another selective alpha7 antagonist, methyllycaconitine (0.05-5 microM), did not strongly inhibit this choline-induced depolarization. Furthermore, the choline-sensitive nAChRs showed little desensitization over 10 s of application with choline (10-30 mM). These results indicate that functional alpha7* nAChRs are significantly present on denervated muscle, and that these receptors display unusual functional and pharmacological characteristics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alpha-conotoxin Arenatus IB[V11L,V16D] [corrected] is a potent and selective antagonist at rat and human native alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Nov;327(2):529-37. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.142943. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18664588 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunits with a C2 cytoplasmic loop yellow fluorescent protein insertion form functional receptors.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009 Jun;30(6):828-41. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.78. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009. PMID: 19498423 Free PMC article.
-
Rat nicotinic ACh receptor alpha7 and beta2 subunits co-assemble to form functional heteromeric nicotinic receptor channels.J Physiol. 2002 Apr 15;540(Pt 2):425-34. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013847. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11956333 Free PMC article.
-
[Dual Roles of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Expressed in Immune Cells in T Cell Differentiation -α7 nAChRs Exert Different Actions between Antigen-presenting Cells and CD4+ T Cells].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020;140(12):1421-1425. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00151. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 33268683 Review. Japanese.
-
Neurogenic and myogenic regulation of skeletal muscle formation: a critical re-evaluation.Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Oct;44(2):119-40. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90035-3. Prog Neurobiol. 1994. PMID: 7831474 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates neuromuscular dysfunction in an experimental rat model of immobilization.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 14;8(49):85537-85548. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20246. eCollection 2017 Oct 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29156739 Free PMC article.
-
Unbalanced Peptidergic Inhibition in Superficial Neocortex Underlies Spike and Wave Seizure Activity.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 24;35(25):9302-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4245-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26109655 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of basal lamina components in neuromotor synapses of children with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 16;8(8):e70288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070288. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23976945 Free PMC article.
-
GTS-21 attenuates loss of body mass, muscle mass, and function in rats having systemic inflammation with and without disuse atrophy.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Nov;470(11):1647-1657. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2180-6. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 30006848 Free PMC article.
-
18F-ASEM PET/MRI targeting alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor can reveal skeletal muscle denervation.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Jan 22;14(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01067-9. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 38252356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albuquerque EX, Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Castro NG, Schrattenholz A, Barbosa CT, Bonfante-Cabarcas R, Aracava Y, Eisenberg HM, Maelicke A. Properties of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: pharmacological characterization and modulation of synaptic function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;280:1117–1136. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EFR, Cortes WS, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Choline is a selective agonist of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the rat brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;9:2734–2742. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira EF, Wonnacott S, Albuquerque EX. Blockade of nicotinic currents in hippocampal neurons defines methyllycaconitine as a potent and specific receptor antagonist. Mol Pharmacol. 1992;41:802–808. - PubMed
-
- Anand R, Peng X, Lindstrom J. Homomeric and native alpha 7 acetylcholine receptors exhibit remarkably similar but non-identical pharmacological properties, suggesting that the native receptor is a heteromeric protein complex. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:241–246. - PubMed
-
- Anzai K, Kobayashi S, Kotake H, Murakami H, Korematsu K, Nonaka I. Neural BC1 RNA in mouse skeletal muscle is a denervation-induced RNA whose expression is developmentally regulated. Neurosci Lett. 1996;216:81–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

