Variation in large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from hair cells along the chicken basilar papilla
- PMID: 12562934
- PMCID: PMC2342658
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029785
Variation in large-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from hair cells along the chicken basilar papilla
Abstract
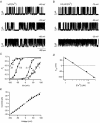
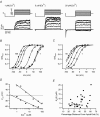
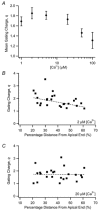
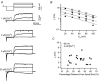
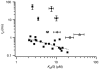
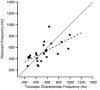
The mechanism for electrical tuning in non-mammalian hair cells rests within the widely diverse kinetics of functionally distinct, large-conductance potassium channels (BK), thought to result from alternative splicing of the pore-forming alpha subunit and variable co-expression with an accessory beta subunit. Inside-out patches from hair cells along the chicken basilar papilla revealed 'tonotopic' gradations in calcium sensitivity and deactivation kinetics. The resonant frequency for the hair cell from which the patch was taken was estimated from deactivation rates, and this frequency reasonably matched that predicted from the originating cell's tonotopic location. The rates of deactivation for native BK channels were much faster than rates reported for cloned chicken BK channels including both alpha and beta subunits. This result was surprising since patches were pulled from hair cells in the apical half of the papilla where beta subunits are most highly expressed. Heterogeneity in the properties of native chicken BK channels implies a high degree of molecular variation and hinders our ability to identify those molecular constituents.
Figures


References
-
- Atkinson NS, Robertson GA, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991;253:551–555. - PubMed
-
- Bers DM, Patton CW, Nuccitelli R. A practical guide to the preparation of Ca2+ buffers. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;40:3–29. - PubMed
-
- Butler A, Tsunoda S, McCobb DP, Wei A, Salkoff L. mSlo, a complex mouse gene encoding ‘maxi’ calcium-activated potassium channels. Science. 1993;261:221–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

