Allosteric regulation and spatial distribution of kainate receptors bound to ancillary proteins
- PMID: 12562952
- PMCID: PMC2342651
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033076
Allosteric regulation and spatial distribution of kainate receptors bound to ancillary proteins
Abstract
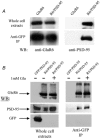
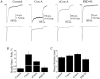
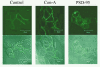
A diverse range of accessory proteins regulates the behaviour of most ligand- and voltage-gated ion channels. For glutamate receptor 6 (GluR6) kainate receptors, two unrelated proteins, concanavalin-A (Con-A) and postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95), bind to extra- and intracellular domains, respectively, but are reported to exert similar effects on GluR6 desensitization behaviour. We have tested the hypothesis that distinct allosteric binding sites control GluR6 receptors via a common transduction pathway. Rapid agonist application to excised patches revealed that neither Con-A nor PSD-95 affect the onset of desensitization. The rate of desensitization elicited by 10 mM L-glutamate was similar in control (taufast = 5.5 +/- 0.4 ms), Con-A-treated patches (taufast = 6.1 +/- 0.5 ms) and patches containing PSD-95 and GluR6 receptors (taufast = 4.7 +/- 0.6 ms). Likewise, the time course of recovery from GluR6 desensitization was similar in both control and Con-A conditions, whereas PSD-95 accelerated recovery almost twofold. Peak and steady-state (SS) dose-response relationships to glutamate were unchanged by lectin treatment (e.g. control, EC50(SS) = 31 +/- 28 microM vs Con-A, EC50(SS) = 45 +/- 9 microM, n = 6), suggesting that Con-A does not convert non-conducting channels with high agonist affinity into an open conformation. Instead, we demonstrate that the effects of Con-A on macroscopic responses reflect a shift in the relative contribution of different open states of the channel. In contrast, the effect of PSD-95 on recovery behaviour suggests that the association between kainate receptors and cytoskeletal proteins regulates signalling at glutamatergic synapses. Our results show that Con-A and PSD-95 regulate kainate receptors via distinct allosteric mechanisms targeting selective molecular steps in the transduction pathway.
Figures





References
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron. 2000;28:165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Sun Y, Chen G-Q, Gouaux E. Structure of a glutamate-receptor ligand-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature. 1998;395:913–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

