Acute shifts of baroreflex control of renal sympathetic nerve activity induced by treadmill exercise in rats
- PMID: 12562953
- PMCID: PMC2342807
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033050
Acute shifts of baroreflex control of renal sympathetic nerve activity induced by treadmill exercise in rats
Abstract
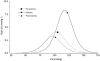
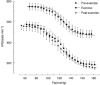
The present study aimed to investigate whether there was a resetting of the baroreflex control of renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) and heart rate (HR) during exercise. Wistar female rats (n = 11) were chronically implanted with catheters for the measurement of systemic arterial (Pa) and central venous pressures and with electrodes for measurement of RSNA and electrocardiogram (ECG) at least 3 days before study. The baroreflex curve for RSNA was determined by changing Pa using rapid intravenous infusions of phenylephrine and nitroprusside. The baroreflex response curves for RSNA and HR were characterized by an inverse sigmoid function curve from which the response range, gain, centering point and minimum response were estimated. Exercise shifted the Pa-RSNA baroreflex curve upward and to the right and was associated with increases in response range of 122 +/- 44 % (P < 0.05), maximum response of 173 +/- 40 % (P < 0.05), maximum gain of 149 +/- 66 % (P < 0.05) and midpoint pressure of 15 +/- 5 mmHg (P < 0.05) compared with the pre-exercise level. After cessation of exercise, the Pa-RSNA baroreflex curve was suppressed vertically with a significant decrease in maximum response of 57 +/- 14 % (P < 0.05) compared with the pre-exercise level. These data suggest that the right-upward shift of baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity may play a critical role in raising and stabilizing Pa during exercise. The suppression of the baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity may partly explain the post-exercise inhibition of sympathetic nerve activity and contribute to the post-exercise hypotension.
Figures



References
-
- Bennett T, Wilcox RG, Macdonald IA. Post-exercise reduction of blood pressure in hypertensive men is not due to acute impairment of baroreflex function. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984;67:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Bishop VS. Carotid baroreflex control of blood pressure and heart rate in men during dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1994;77:491–492. - PubMed
-
- Collins HL, Rodenbaugh DW, Di Carlo SE. Central blockade of vasopressin V(1) receptors attenuates postexercise hypotension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;281:R375–380. - PubMed
-
- Di Carlo SE, Bishop VS. Onset of exercise shifts operating point of arterial baroreflex to higher pressures. Am J Physiol. 1992;262:H303–307. - PubMed
-
- Di Carlo SE, Bishop VS. Central baroreflex resetting as a means of increasing and decreasing sympathetic outflow and arterial pressure. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;940:324–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

