Expression of IGF-I splice variants in young and old human skeletal muscle after high resistance exercise
- PMID: 12562960
- PMCID: PMC2342624
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032136
Expression of IGF-I splice variants in young and old human skeletal muscle after high resistance exercise
Abstract
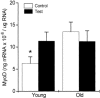
The mRNA expression of two splice variants of the insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) gene, IGF-IEa and mechano growth factor (MGF), were studied in human skeletal muscle. Subjects (eight young, aged 25-36 years, and seven elderly, aged 70-82 years) completed 10 sets of six repetitions of single legged knee extensor exercise at 80 % of their one repetition maximum. Muscle biopsy samples were obtained from the quadriceps muscle of both the control and exercised legs 2.5 h after completion of the exercise bout. Expression levels of the IGF-I mRNA transcripts were determined using real-time quantitative RT-PCR with specific primers. The resting levels of MGF were significantly (approximately 100-fold) lower than those of the IGF-IEa isoform. No difference was observed between the resting levels of the two isoforms between the two subject groups. High resistance exercise resulted in a significant increase in MGF mRNA in the young, but not in the elderly subjects. No changes in IGF-IEa mRNA levels were observed as a result of exercise in either group. The mRNA levels of the transcription factor MyoD were greater at rest in the older subjects (P < 0.05), but there was no significant effect of the exercise bout. Electrophoretic separation of myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoforms showed the older subjects to have a lower (P < 0.05) percentage of MHC-II isoforms than the young subjects. However, no association was observed between the composition of the muscle and changes in the IGF-I isoforms with exercise. The data from this study show an attenuated MGF response to high resistance exercise in the older subjects, indicative of age-related desensitivity to mechanical loading. The data in young subjects indicate that the MGF and IGF-IEa isoforms are differentially regulated in human skeletal muscle.
Figures
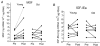
Comment in
-
IGF-I isoforms and ageing skeletal muscle: an 'unresponsive' hypertrophy agent?J Physiol. 2003 Feb 15;547(Pt 1):2. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033738. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12589001 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The effect of recombinant human growth hormone and resistance training on IGF-I mRNA expression in the muscles of elderly men.J Physiol. 2004 Feb 15;555(Pt 1):231-40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.051722. Epub 2003 Oct 17. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14565994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of eccentric cycling exercise on IGF-I splice variant expression in the muscles of young and elderly people.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008 Aug;18(4):447-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00714.x. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008. PMID: 18067523
-
Skeletal muscle IGF-I isoform expression in healthy women after isometric exercise.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2006 Oct-Dec;16(5-6):373-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2006.09.005. Epub 2006 Nov 14. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2006. PMID: 17107821
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I E peptides: implications for aging skeletal muscle.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010 Feb;20(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.00997.x. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2010. PMID: 19883387 Review.
-
Gene expression in muscle in response to exercise.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003;24(2-3):121-6. doi: 10.1023/a:1026041228041. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2003. PMID: 14609023 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Alternatively Spliced Messenger RNA (mRNA) Isoforms of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 (IGF1) in Selected Human Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):6995. doi: 10.3390/ijms21196995. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of eccentric exercise on mRNA expression of skeletal muscle regulators.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007 Nov;101(4):473-80. doi: 10.1007/s00421-007-0521-9. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17661068
-
PAX7 and MyoD Proteins Expression in Response to Eccentric and Concentric Resistance Exercise in Active Young Men.Cell J. 2023 Feb 1;25(2):135-142. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.557440.1055. Cell J. 2023. PMID: 36840460 Free PMC article.
-
Igf-I and fgf-2 responses to wingate anaerobic test in older men.J Sports Sci Med. 2007 Jun 1;6(2):227-32. eCollection 2007. J Sports Sci Med. 2007. PMID: 24149333 Free PMC article.
-
IGF1 promotes human myotube differentiation toward a mature metabolic and contractile phenotype.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 May 1;326(5):C1462-C1481. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00654.2023. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38690930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams GR, Haddad F. The relationships among IGF-I, DNA content, and protein accumulation during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol. 1996;81:2509–2516. - PubMed
-
- Adams GR, McCue SA. Localized infusion of IGF-I results in skeletal muscle hypertrophy in rats. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84:1716–1722. - PubMed
-
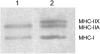
- Andersen JL, Aagaard P. Myosin heavy chain IIX overshoot in human skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2000;23:1095–1104. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JL, Mohr T, Biering-Sorensen F, Galbo H, Kjaer M. Myosin heavy chain isoform transformation in single fibres from m. vastus lateralis in spinal cord injured individuals: effects of long-term functional electrical stimulation (FES) Pflugers Arch. 1996;431:513–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

