Low doses of ethanol and a neuroactive steroid positively interact to modulate rat GABA(A) receptor function
- PMID: 12562992
- PMCID: PMC2342575
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032300
Low doses of ethanol and a neuroactive steroid positively interact to modulate rat GABA(A) receptor function
Abstract
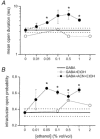
Fast inhibitory responses in the central nervous system are mediated by the GABA(A) receptor. The activation and function of the GABA(A) receptor can be modulated by a variety of compounds including benzodiazepines, barbiturates and neuroactive steroids. Modulation of the GABA(A) receptor function by ethanol has been observed in some but not all studies. We have studied the effect of ethanol at concentrations corresponding to light intoxication on the function of the recombinant GABA(A) receptor containing alpha1beta2gamma2 subunits. The experiments were performed both in the absence and presence of low, subthreshold concentrations of a neuroactive steroid. The results demonstrate that, in the presence of the steroid, 0.05 % (9 mM) ethanol potentiates the GABA(A) receptor function by increasing the channel mean open duration. No effect was observed on the channel closed time durations. The data suggest that ethanol influences channel closing with no effect on the affinity of the receptor for GABA or the channel opening rate constant.
Figures

References
-
- Aguayo LG. Ethanol potentiates the GABAA-activated Cl− current in mouse hippocampal and cortical neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;187:127–130. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K, editors. Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. 2. New York: John Wiley; 1992.
-
- Baulieu EE. Neurosteroids: of the nervous system, by the nervous system, for the nervous system. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1997;52:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Celentano JJ, Gibbs TT, Farb DH. Ethanol potentiates GABA- and glycine-induced chloride currents in chick spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1988;455:377–380. - PubMed
-
- Criswell HE, McCown TJ, Ming Z, Mueller RA, Breese GR. Interactive role for neurosteroids in ethanol enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid-gated currents from dissociated substantia nigra reticulata neurons. J Pharm Exp Ther. 1999;291:1054–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

