Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors activate a calcium-sensitive transient receptor potential-like conductance in rat hippocampus
- PMID: 12562994
- PMCID: PMC2342598
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.032961
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors activate a calcium-sensitive transient receptor potential-like conductance in rat hippocampus
Abstract
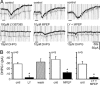
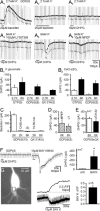
In CA3 pyramidal neurons from organotypic slice cultures, activation of G(q)-coupled group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) induces a non-selective cationic conductance that enhances excitability. We have found that this response shares several properties with conductances that are mediated by the transient receptor potential (TRP) family of ion channels, including inhibition by La(3+), 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborane (2APB), cis-N-(2-phenylcyclopentyl)azacyclotridec-1-en-2-amine (MDL 12,330A) and a doubly rectifying current-voltage relationship. Stimulation of mGluR1 and mGluR5 converged to activate the TRP-like conductance in a synergistic manner, and activation of either subtype alone produced only a fraction of the normal response. Activation of the cationic current required elevated intracellular Ca(2+). Chelating intracellular Ca(2+) or blocking Ca(2+) entry through voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels attenuated responses to the activation of mGluRs. Conversely, raising intracellular Ca(2+) potentiated mGluR activation of the TRP-like conductance. Under control conditions, blocking G protein activation using intracellular GDPbetaS with or without N-(2, 6-dimethylphenylcarbamoylmethyl) triethylammonium chloride (QX-314) prevented mGluR-mediated activation of the TRP-like conductance. Following G protein blockade, however, the coupling between mGluRs 1 and/or 5 and the TRP-like conductance was rescued by increasing intracellular Ca(2+). This suggests that a G protein-independent signalling pathway is also activated by group I mGluRs. Such a pathway may represent an alternative transduction mechanism to maintain metabotropic responses under conditions where G proteins are functionally uncoupled from their cognate receptors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors coupled to IP3 production mediate inhibition of IAHP in rat dentate granule neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1996 Oct;76(4):2691-700. doi: 10.1152/jn.1996.76.4.2691. J Neurophysiol. 1996. PMID: 8899638
-
Modulation of intracellular calcium mobilization and GABAergic currents through subtype-specific metabotropic glutamate receptors in neonatal rat hippocampus.Brain Res Bull. 2010 Jan 15;81(1):73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2009.07.011. Brain Res Bull. 2010. PMID: 19628026
-
Slow feedback inhibition in the CA3 area of the rat hippocampus by synergistic synaptic activation of mGluR1 and mGluR5.J Physiol. 2002 Nov 1;544(3):793-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030163. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12411524 Free PMC article.
-
The modulation of calcium currents by the activation of mGluRs. Functional implications.Mol Neurobiol. 1996 Aug;13(1):81-95. doi: 10.1007/BF02740753. Mol Neurobiol. 1996. PMID: 8892337 Review.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999 Jan;29(1):83-120. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(98)00050-2. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999. PMID: 9974152 Review.
Cited by
-
Group I mGluR activation enhances Ca(2+)-dependent nonselective cation currents and rhythmic bursting in main olfactory bulb external tufted cells.J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 23;29(38):11943-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0206-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19776280 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors in the lateral superior olive activate TRP-like channels: age- and experience-dependent regulation.J Neurophysiol. 2007 May;97(5):3365-75. doi: 10.1152/jn.00686.2006. Epub 2007 Mar 21. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17376850 Free PMC article.
-
DAG-sensitive and Ca(2+) permeable TRPC6 channels are expressed in dentate granule cells and interneurons in the hippocampal formation.Hippocampus. 2013 Mar;23(3):221-32. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22081. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23193081 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-operated cation channels formed by TRPC4 and TRPC5.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005 Apr;371(4):266-76. doi: 10.1007/s00210-005-1055-5. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15902430 Review.
-
TRPC3 channels are necessary for brain-derived neurotrophic factor to activate a nonselective cationic current and to induce dendritic spine formation.J Neurosci. 2007 May 9;27(19):5179-89. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5499-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17494704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor AM, Garthwaite J. Frequency detection and temporally dispersed synaptic signal association through a metabotropic glutamate receptor pathway. Nature. 1997;385:74–77. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29672–29680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

