Phosphorylation of the myosin phosphatase targeting subunit and CPI-17 during Ca2+ sensitization in rabbit smooth muscle
- PMID: 12563012
- PMCID: PMC2342583
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.029306
Phosphorylation of the myosin phosphatase targeting subunit and CPI-17 during Ca2+ sensitization in rabbit smooth muscle
Abstract
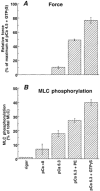
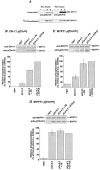
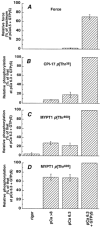
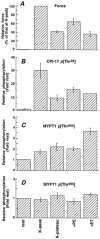
Myosin phosphatase (MLCP) plays a critical regulatory role in the Ca(2+) sensitivity of myosin phosphorylation and smooth muscle contraction. It has been suggested that phosphorylation at Thr(695) of the MLCP regulatory subunit (MYPT1) and at Thr(38) of the MLCP inhibitor protein CPI-17 results in inhibition of MLCP activity. We have previously demonstrated that CPI-17 Thr(38) phosphorylation plays an important role in G-protein-mediated inhibition of MLCP in tonic arterial smooth muscle. Here, we attempted to evaluate the function of MYPT1 in phasic rabbit portal vein (PV) and vas deferens (VD) smooth muscles. Using site- and phospho-specific antibodies, phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr(695) and CPI-17 Thr(38) was examined along with MYPT1 Thr(850), which is a non-inhibitory Rho-kinase site. We found that both CPI-17 Thr(38) and MYPT1 Thr(850) were phosphorylated in response to agonists or GTPgammaS concurrently with contraction and myosin phosphorylation in alpha-toxin-permeabilized PV tissues. In contrast, phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr(695) did not increase. Comparable results were also obtained in both permeabilized and intact VD. The Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 and the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor GF109203X suppressed phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr(850) and CPI-17 Thr(38), respectively, in intact VD while MYPT1 Thr(695) phosphorylation was insensitive to both inhibitors. These results indicate that phosphorylation of MYPT1 Thr(695) is independent of stimulation of G-proteins, Rho-kinase or PKC. In the phasic PV, phosphorylation of CPI-17 Thr(38) may contribute towards inhibition of MLCP while the phasic visceral VD, which has a low CPI-17 concentration, probably utilizes other Ca(2+) sensitizing mechanisms for inhibiting MLCP besides phosphorylation of MYPT1 and CPI-17.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of CPI-17 and myosin phosphatase correlates with Ca(2+) sensitivity of protein kinase C-induced contraction in rabbit smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2001 Sep 1;535(Pt 2):553-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00553.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11533144 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists trigger G protein-mediated activation of the CPI-17 inhibitor phosphoprotein of myosin light chain phosphatase to enhance vascular smooth muscle contractility.J Biol Chem. 2000 Apr 7;275(14):9897-900. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.14.9897. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10744661
-
Histamine-induced vasoconstriction involves phosphorylation of a specific inhibitor protein for myosin phosphatase by protein kinase C alpha and delta isoforms.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 3;276(31):29072-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103206200. Epub 2001 Jun 7. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11397799
-
Protein kinase network in the regulation of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain.Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Jun;248(1-2):105-14. doi: 10.1023/a:1024180101032. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12870661 Review.
-
Rho-Mancing to Sensitize Calcium Signaling for Contraction in the Vasculature: Role of Rho Kinase.Adv Pharmacol. 2017;78:303-322. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Adv Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28212799 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of PKC and RhoA/ROCK pathways in the spontaneous phasic activity in the rectal smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Apr 15;304(8):G723-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00473.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23413252 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the Ca(2+)-dependent tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in tonic depolarization-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015 Dec;36(6):479-89. doi: 10.1007/s10974-015-9416-2. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2015. PMID: 26150074 Review.
-
Myogenic vasoconstriction requires G12/G13 and LARG to maintain local and systemic vascular resistance.Elife. 2019 Sep 24;8:e49374. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49374. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31549965 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboxane A2-induced contraction of rat caudal arterial smooth muscle involves activation of Ca2+ entry and Ca2+ sensitization: Rho-associated kinase-mediated phosphorylation of MYPT1 at Thr-855, but not Thr-697.Biochem J. 2005 Aug 1;389(Pt 3):763-74. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050237. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15823093 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in regulating alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated vascular smooth muscle contraction.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Aug 23;17(1):67. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-67. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20727219 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Borman MA, MacDonald JA, Murányi A, Hartshorne DJ, Haystead TA. Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase-associated kinase induces Ca2+ sensitization via myosin phosphatase inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:23441–23446. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G. Noradrenaline and ATP: cotransmitters and neuromodulators. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995;46:365–384. - PubMed
-
- Butler TM, Narayan SR, Mooers Su, Siegman MJ. Rapid turnover of myosin light chain phosphate during cross-bridge cycling in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1994;36:C1160–1166. - PubMed
-
- Chen YH, Chen MX, Alessi DR, Campbell DG, Shanahan C, Cohen P, Cohen PTW. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the 110 kDa and 21 kDa regulatory subunits of smooth muscle protein phosphatase 1M. FEBS Lett. 1994;356:51–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

