Centre and surround responses of marmoset lateral geniculate neurones at different temporal frequencies
- PMID: 12563014
- PMCID: PMC2342578
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.027748
Centre and surround responses of marmoset lateral geniculate neurones at different temporal frequencies
Abstract
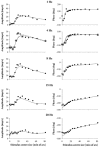
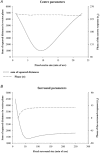
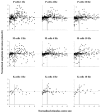
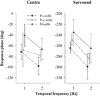
The responses of marmoset lateral geniculate neurones to stimuli that were composed of a sinusoidally modulating centre stimulus and a surround that was modulated in counterphase were measured. The size of the stimulus centre was varied. These measurements were repeated at different temporal frequencies between 1 and 30 Hz. The response amplitudes and phases depended in a characteristic manner on the stimulus centre size. The response behaviour could be modelled by assuming Gaussian responsivity profiles of the cells' receptive field (RF) centres and surrounds and a phase delay in the RF surround responses, relative to the centre, enabling the description of RF centre and surround response characteristics. We found that the RF centre-to-surround phase difference increased linearly with increasing temporal frequency, indicating a constant delay difference of about 4.5 to 6 ms. A linear model, including low-pass filters, a lead lag stage and a delay, was used to describe the mean RF centre and surround responses. The separate RF centre and surround responses were less band pass than the full receptive field responses of the cells. The linear model provided less satisfactory fits to M-cell responses than to those of P-cells, indicating additional nonlinearities.
Figures

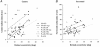
Similar articles
-
Linking lateral interactions in flicker perception to lateral geniculate nucleus cell responses.J Physiol. 2007 Jun 15;581(Pt 3):1083-100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.129486. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17412770 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral interactions in the perception of flicker and in the physiology of the lateral geniculate nucleus.J Vis. 2004 Aug 9;4(7):643-63. doi: 10.1167/4.7.10. J Vis. 2004. PMID: 15330708
-
Influence of contrast on the responses of marmoset lateral geniculate cells to drifting gratings.J Neurophysiol. 2001 Jan;85(1):235-46. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.85.1.235. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11152723
-
Receptive field dimensions of lateral geniculate cells in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus).Vision Res. 1997 Aug;37(16):2171-81. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(97)00041-2. Vision Res. 1997. PMID: 9578900
-
Temporal properties of spatial frequency tuning of surround suppression in the primary visual cortex and the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Jun;31(11):2086-100. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07235.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20604803
Cited by
-
Linking lateral interactions in flicker perception to lateral geniculate nucleus cell responses.J Physiol. 2007 Jun 15;581(Pt 3):1083-100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.129486. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17412770 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission of colour and acuity signals by parvocellular cells in marmoset monkeys.J Physiol. 2011 Jun 1;589(Pt 11):2795-812. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.194076. Epub 2011 Apr 11. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21486786 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission of blue (S) cone signals through the primate lateral geniculate nucleus.J Physiol. 2008 Dec 15;586(24):5947-67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.161893. Epub 2008 Oct 27. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18955378 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatic and spatial properties of parvocellular cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the marmoset (Callithrix jacchus).J Physiol. 2004 May 15;557(Pt 1):229-45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.058065. Epub 2004 Mar 26. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15047769 Free PMC article.
-
Random wiring in the midget pathway of primate retina.J Neurosci. 2006 Apr 12;26(15):3908-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4891-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16611806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benardete EA, Kaplan E. The receptive field or the primate P retinal ganglion cells, I: Linear systems. Vis Neurosci. 1997;14:169–185. - PubMed
-
- Benardete EA, Kaplan E. The dynamics of primate M retinal ganglion cells. Vis Neurosci. 1999;16:355–368. - PubMed
-
- Benardete EA, Kaplan E, Knight BW. Contrast gain control in the primate retina: P cells are not X-like, some M cells are. Vis Neurosci. 1992;8:483–486. - PubMed
-
- Croner LJ, Kaplan E. Receptive fields of P and M ganglion cells across the primate retina. Vision Res. 1995;35:7–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

